Prenatal protein malnutrition alters the proportion but not numbers of parvalbumin-immunoreactive interneurons in the hippocampus of the adult Sprague-Dawley rat
- PMID: 21902887
- PMCID: PMC4139119
- DOI: 10.1179/147683011X13009738172396
Prenatal protein malnutrition alters the proportion but not numbers of parvalbumin-immunoreactive interneurons in the hippocampus of the adult Sprague-Dawley rat
Abstract
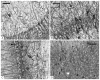
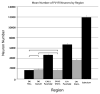
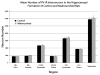
Prenatal protein malnutrition alters the structure and function of the adult rat hippocampal formation. The current study examines the effect of prenatal protein malnutrition on numbers of parvalbumin-immunoreactive (PV-IR) GABAergic interneurons, which are important for perisomatic inhibition of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Brain sections from prenatally protein malnourished and normally nourished rats were stained for parvalbumin and PV-IR neurons were quantified using stereology in the dentate gyrus, CA3/2 and CA1 subfields, and the subiculum for both cerebral hemispheres. Results demonstrated that prenatal malnutrition did not affect the number of PV-IR interneurons in the hippocampus. Since prenatal protein malnutrition reduces total neuron numbers in the CA1 subfield (1), this results in an altered ratio of PV-IR interneurons to total neuronal numbers (from 1:22.9 in controls to 1:20.5 in malnourished rats). Additionally, there was no hemispheric asymmetry of either PV-IR neuron numbers or ratio of PV-IR:total neuron numbers.
Figures




References
-
- Lister JP, Tonkiss J, Blatt GJ, Kemper TL, Debassio WA, Galler JR, et al. Asymmetry of neuron numbers in the hippocampal formation of prenatally malnourished and normally nourished rats: a stereological investigation. Hippocampus. 2006;16(11):946–58. - PubMed
-
- Galler JR, Shumsky JS, Morgane PJ. Malnutrition and brain development. In: Walker W, Watkins J, editors. Nutrition in pediatrics. Neuilly-sur-Seine, France: B.C. Decker, Inc; 1996. pp. 196–212.
-
- Morgane PJ, Mokler DJ, Galler JR. Effects of prenatal protein malnutrition on the hippocampal formation. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2002;26(4):471–83. - PubMed
-
- Tonkiss J, Galler J, Morgane PJ, Bronzino JD, Austin-LaFrance RJ. Prenatal protein malnutrition and postnatal brain function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993;678:215–27. - PubMed
-
- Austin KB, Bronzino J, Morgane PJ. Prenatal protein malnutrition affects synaptic potentiation in the dentate gyrus of rats in adulthood. Brain Res. 1986;394(2):267–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
