Comparison of training methods to improve walking in persons with chronic spinal cord injury: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 21903010
- PMCID: PMC3152808
- DOI: 10.1179/2045772311Y.0000000018
Comparison of training methods to improve walking in persons with chronic spinal cord injury: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: To compare two forms of device-specific training - body-weight-supported (BWS) ambulation on a fixed track (TRK) and BWS ambulation on a treadmill (TM) - to comprehensive physical therapy (PT) for improving walking speed in persons with chronic, motor-incomplete spinal cord injury (SCI).
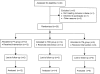
Methods: Thirty-five adult subjects with a history of chronic SCI (>1 year; AIS 'C' or 'D') participated in a 13-week (1 hour/day; 3 days per week) training program. Subjects were randomized into one of the three training groups. Subjects in the two BWS groups trained without the benefit of additional input from a physical therapist or gait expert. For each training session, performance values and heart rate were monitored. Pre- and post-training maximal 10-m walking speed, balance, muscle strength, fitness, and quality of life were assessed in each subject.
Results: All three training groups showed significant improvement in maximal walking speed, muscle strength, and psychological well-being. A significant improvement in balance was seen for PT and TRK groups but not for subjects in the TM group. In all groups, post-training measures of fitness, functional independence, and perceived health and vitality were unchanged.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that persons with chronic, motor-incomplete SCI can improve walking ability and psychological well-being following a concentrated period of ambulation therapy, regardless of training method. Improvement in walking speed was associated with improved balance and muscle strength. In spite of the fact that we withheld any formal input of a physical therapist or gait expert from subjects in the device-specific training groups, these subjects did just as well as subjects receiving comprehensive PT for improving walking speed and strength. It is likely that further modest benefits would accrue to those subjects receiving a combination of device-specific training with input from a physical therapist or gait expert to guide that training.
Figures






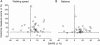
References
-
- Jackson AB, Dijkers M, DeVivo MJ, Poczatek RB. A demographic profile of new traumatic spinal cord injuries: change and stability over 30 years. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2004;85(11):1740–8 - PubMed
-
- Calancie B, Molano MR, Broton JG. Epidemiology and demography of acute spinal cord injury in a large urban setting. J Spinal Cord Med 2005;28(2):92–6 - PubMed
-
- Behrman AL, Harkema SJ. Locomotor training after human spinal cord injury: a series of case studies. Phys Ther 2000;80(7):688–700 - PubMed
-
- Wernig A, Müller S. Laufband locomotion with body weight support improved walking in persons with severe spinal cord injuries. Paraplegia 1992;30(4):229–38 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
