Single units in the medial prefrontal cortex with anxiety-related firing patterns are preferentially influenced by ventral hippocampal activity
- PMID: 21903082
- PMCID: PMC3201792
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.07.027
Single units in the medial prefrontal cortex with anxiety-related firing patterns are preferentially influenced by ventral hippocampal activity
Abstract
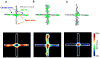
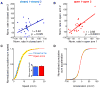
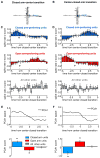
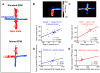
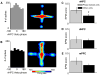
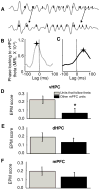
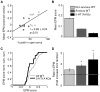
The medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and ventral hippocampus (vHPC) functionally interact during innate anxiety tasks. To explore the consequences of this interaction, we examined task-related firing of single units from the mPFC of mice exploring standard and modified versions of the elevated plus maze (EPM), an innate anxiety paradigm. Hippocampal local field potentials (LFPs) were simultaneously monitored. The population of mPFC units distinguished between safe and aversive locations within the maze, regardless of the nature of the anxiogenic stimulus. Strikingly, mPFC units with stronger task-related activity were more strongly coupled to theta-frequency activity in the vHPC LFP. Lastly, task-related activity was inversely correlated with behavioral measures of anxiety. These results clarify the role of the vHPC-mPFC circuit in innate anxiety and underscore how specific inputs may be involved in the generation of behaviorally relevant neural activity within the mPFC.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

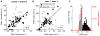

References
-
- Bannerman DM, Deacon RM, Offen S, Friswell J, Grubb M, Rawlins JN. Double dissociation of function within the hippocampus: spatial memory and hyponeophagia. Behav Neurosci. 2002;116:884–901. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman DM, Rawlins JN, McHugh SB, Deacon RM, Yee BK, Bast T, Zhang WN, Pothuizen HH, Feldon J. Regional dissociations within the hippocampus--memory and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;28:273–283. - PubMed
-
- Bartho P, Hirase H, Monconduit L, Zugaro M, Harris KD, Buzsaki G. Characterization of neocortical principal cells and interneurons by network interactions and extracellular features. J Neurophysiol. 2004;92:600–608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

