Sequential vs. concurrent chemoradiation for stage III non-small cell lung cancer: randomized phase III trial RTOG 9410
- PMID: 21903745
- PMCID: PMC3186782
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djr325
Sequential vs. concurrent chemoradiation for stage III non-small cell lung cancer: randomized phase III trial RTOG 9410
Erratum in
- J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Jan 4;104(1):79
Abstract
Background: The combination of chemotherapy with thoracic radiotherapy (TRT) compared with TRT alone has been shown to confer a survival advantage for good performance status patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer. However, it is not known whether sequential or concurrent delivery of these therapies is the optimal combination strategy.
Methods: A total of 610 patients were randomly assigned to two concurrent regimens and one sequential chemotherapy and TRT regimen in a three-arm phase III trial. The sequential arm included cisplatin at 100 mg/m2 on days 1 and 29 and vinblastine at 5 mg/m2 per week for 5 weeks with 63 Gy TRT delivered as once-daily fractions beginning on day 50. Arm 2 used the same chemotherapy regimen as arm 1 with 63 Gy TRT delivered as once-daily fractions beginning on day 1 [corrected]. Arm 3 used cisplatin at 50 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, 29, and 36 with oral etoposide at 50 mg twice daily for 10 weeks on days 1, 2, 5, and 6 with 69.6 Gy delivered as 1.2 Gy twice-daily fractions beginning on day 1. The primary endpoint was overall survival, and secondary endpoints included tumor response and time to tumor progression. Kaplan-Meier analyses were used to assess survival, and toxic effects were examined using the Wilcoxon rank sum test. All statistical tests were two-sided.
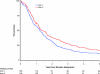
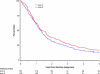
Results: Median survival times were 14.6, 17.0, and 15.6 months for arms 1-3, respectively. Five-year survival was statistically significantly higher for patients treated with the concurrent regimen with once-daily TRT compared with the sequential treatment (5-year survival: sequential, arm 1, 10% [20 patients], 95% confidence interval [CI] = 7% to 15%; concurrent, arm 2, 16% [31 patients], 95% CI = 11% to 22%, P = .046; concurrent, arm 3, 13% [22 patients], 95% CI = 9% to 18%). With a median follow-up time of 11 years, the rates of acute grade 3-5 nonhematologic toxic effects were higher with concurrent than sequential therapy, but late toxic effects were similar.
Conclusion: Concurrent delivery of cisplatin-based chemotherapy with TRT confers a long-term survival benefit compared with the sequential delivery of these therapies.
Figures

Comment in
-
RTOG 94-10: keenly awaited results validating the best therapeutic strategy for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011 Oct 5;103(19):1425-7. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr348. Epub 2011 Sep 8. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011. PMID: 21903746 No abstract available.
-
RE: A phase I trial of radiation dose escalation using accelerated concomitant boost radiotherapy concurrently with weekly carboplatin/paclitaxel in patients with good performance status and Stage IIB-IIIA/B non-small cell lung cancer.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2012 Oct;56(5):574-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1754-9485.2012.02407.x. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23043579 No abstract available.
References
-
- Beahrs OH, Henson DE, Hutter RVP, et al. American Joint Committee on Cancer Manual for Staging of Cancer. Philadelphia, PA: JB Lippincott Co; 1992.
-
- Dillman RO, Seagren SL, Herndon J, et al. A randomized trial of induction chemotherapy plus high-dose radiation versus radiation alone in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:940–945. - PubMed
-
- Sause W, Scott C, Taylor S, et al. Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 88-08 and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 4588: preliminary results of a phase III trial in regionally advanced, unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995;87:198–205. - PubMed
-
- Le Chevalier T, Arriagada R, Quoix E, et al. Radiotherapy alone versus combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy in nonresectable non-small-cell lung cancer: first analysis of a randomized trial in 353 patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991;83:417–423. - PubMed
-
- Schaake-Koning C, Van Den Bogert W, Dalesio O, et al. Effects of concomitant cisplatin and radiotherapy in inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:524–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

