Pretreatment with the probiotic VSL#3 delays transition from inflammation to dysplasia in a rat model of colitis-associated cancer
- PMID: 21903764
- PMCID: PMC3233787
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00167.2011
Pretreatment with the probiotic VSL#3 delays transition from inflammation to dysplasia in a rat model of colitis-associated cancer
Abstract
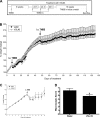
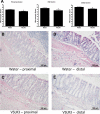
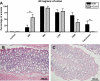
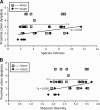
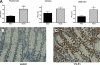
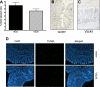
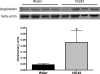
Evidence supports involvement of microflora in the transition of chronic inflammation to neoplasia. We investigated the protective efficacy of the probiotic VSL#3 in a model of colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Chronic colitis was induced in Sprague-Dawley rats by administration of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS), followed 6 wk later by systemic reactivation. To induce colitis-associated dysplasia and cancer, the animals received TNBS (intravenously) twice a week for 10 wk. One group received VSL#3 in drinking water from 1 wk before colitis induction until death. The colons were examined for damage and presence of dysplasia or cancer. Samples were analyzed for cell proliferation and apoptosis, vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression, angiogenic factors, and presence of alkaline sphingomyelinase or phosphatase. Microbial community composition was evaluated by terminal restriction fragment-length polymorphism analysis of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene. None of the probiotic-treated animals developed carcinoma, and no high-grade dysplasia was found in either the proximal or mid colon. In contrast, 29% of the animals in the control group developed carcinoma in one or more regions of the colon. VSL#3-treated animals had significantly less damage than the vehicle treated-controls in all areas of the colon, and this correlated with decreased richness and diversity of the mucosally adherent microbiota. Treatment with the probiotic increased the antiangiogenic factor angiostatin, VDR expression, and alkaline sphingomyelinase. We concluded that pretreatment with the probiotic VSL#3 can attenuate various inflammatory-associated parameters, delaying transition to dysplasia and cancer, thus offering its potential therapeutic use in patients with long-standing colitis.
Figures
References
-
- Alberts DS, Martinez ME, Hess LM, Einspahr JG, Green SB, Bhattacharyya AK, Guillen J, Krutzsch M, Batta AK, Salen G, Fales L, Koonce K, Parish D, Clouser M, Roe D, Lance P, Phoenix and Tucson Gastroenterologist Networks Phase III trial of ursodeoxycholic acid to prevent colorectal adenoma recurrence. J Natl Cancer Inst 97: 846– 853, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Appleyard CB, Morales M, Santiago C. Chronic inflammation alters the contribution of neurokinin receptor subtypes to epithelial function in rat colon. Dig Dis Sci 53: 220– 228, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Appleyard CB, Wallace JL. Reactivation of hapten-induced colitis and its prevention by anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 269: G119– G125, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein CN, Blanchard JF, Kliewer E, Wajda A. Cancer risk in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Cancer 91: 854– 862, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Bibiloni R, Fedorak RN, Tannock GW, Madsen KL, Gionchetti P, Campieri M, De Simone C, Sartor RB. VSL#3 probiotic-mixture induces remission in patients with active ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol 100: 1539– 1546, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

