Interlaboratory reproducibility of DiversiLab rep-PCR typing and clustering of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates
- PMID: 21903821
- PMCID: PMC3347881
- DOI: 10.1099/jmm.0.036046-0
Interlaboratory reproducibility of DiversiLab rep-PCR typing and clustering of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates
Abstract
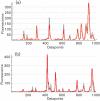
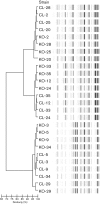
We have investigated the reproducibility of DiversiLab rep-PCR fingerprints between two laboratories with the aim of determining if the fingerprints and clustering are laboratory-specific or portable. One-hundred non-duplicate Acinetobacter baumannii isolates were used in this study. DNA isolation and rep-PCR were each performed separately in two laboratories and rep-PCR patterns generated in laboratory A were compared with those from laboratory B. Twelve A. baumannii isolates processed in laboratory A showed ≥98 % pattern similarity with the corresponding 12 isolates tested in laboratory B and were considered identical. Sixty-four isolates showed 95-97.9 % similarity with their corresponding isolates. Twenty-three isolates showed 90-94 % similarity with the corresponding isolates, while one isolate showed only 87.4 % similarity. However, intra-laboratory clustering was conserved: isolates that clustered in laboratory A also clustered in laboratory B. While clustering was conserved and reproducible at two different laboratories, demonstrating the robustness of rep-PCR, interlaboratory comparison of individual isolate fingerprints showed more variability. This comparison allows conclusions regarding clonality to be reached independent of the laboratory where the analysis is performed.
Figures
References
-
- Brolund A., Hæggman S., Edquist P. J., Gezelius L., Olsson-Liljequist B., Wisell K. T., Giske C. G. (2010). The DiversiLab system versus pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: characterisation of extended spectrum β-lactamase producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Microbiol Methods 83, 224–23010.1016/j.mimet.2010.09.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carretto E., Barbarini D., Farina C., Grosini A., Nicoletti P., Manso E., APSI ‘Acinetobacter Study Group’, Italy (2008). Use of the DiversiLab semiautomated repetitive-sequence-based polymerase chain reaction for epidemiologic analysis on Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in different Italian hospitals. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 60, 1–710.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2007.07.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carretto E., Barbarini D., Dijkshoorn L., van der Reijden T. J. K., Brisse S., Passet V., Farina C., APSI Acinetobacter Study Group (2011). Widespread carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clones in Italian hospitals revealed by a multicenter study. Infect Genet Evol 11, 1319–132610.1016/j.meegid.2011.04.024 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Church D. L., Chow B. L., Lloyd T., Gregson D. B. (2011). Comparison of automated repetitive-sequence-based polymerase chain reaction and spa typing versus pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 69, 30–3710.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2010.09.010 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

