Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging of sildenafil treatment of embolic stroke in aged rats
- PMID: 21903952
- PMCID: PMC3226838
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.622092
Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging of sildenafil treatment of embolic stroke in aged rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Sildenafil provides restorative therapeutic benefits in the treatment of experimental stroke. The majority of experimental studies on treatment of stroke have been performed in young animals; however, stroke is primarily a disease of the aged. Thus, using MRI, we evaluated the effects of sildenafil treatment of embolic stroke in aged animals.
Methods: Aged male Wistar rats (18 months) were subjected to embolic stroke and treated daily with saline (n=10) or with sildenafil (n=10) initiated at 24 hours and subsequently for 7 days after onset of ischemia. MRI measurements were performed at 24 hours and weekly to 6 weeks after embolization.
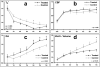
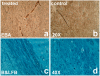
Results: MRI and histological measurements demonstrated that sildenafil treatment of aged rats significantly enhanced angiogenesis and axonal remodeling after stroke compared to saline-treated aged rats. Local cerebral blood flow in the angiogenic area was elevated and expansion of the ipsilateral ventricle and, consequently, brain atrophy was significantly reduced in the sildenafil-treated rats.
Conclusions: Treatment of embolic stroke in aged rats with sildenafil significantly augments angiogenesis and axonal remodeling, which increased local blood flow and reduced expansion of the ipsilateral ventricle 6 weeks after stroke compared to control aged rats. MRI can be used to investigate brain repair after stroke in aged rats.
Figures

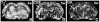
References
-
- Chen RL, Balami JS, Esiri MM, Chen LK, Buchan AM. Ischemic stroke in the elderly: An overview of evidence. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6:256–265. - PubMed
-
- Keller JN, Gee J, Ding Q. The proteasome in brain aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2002;1:279–293. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Zhang RL, Wang Y, Zhang CL, Zhang ZG, Meng H, Chopp M. Functional recovery in aged and young rats after embolic stroke-treatment with a phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor. Stroke. 2005;36:847–852. - PubMed
-
- Futrell N, Garcia JH, Peterson E, Millikan C. Embolic stroke in aged rats. Stroke. 1991;22:1582–1591. - PubMed
-
- Badan I, Buchhold B, Hamm A, Gratz M, Walker LC, Platt D, Kessler C, Popa-Wagner A. Accelerated glial reactivity to stroke in aged rats correlates with reduced functional recovery. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23:845–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

