Non-invasive measurement of local pulse pressure by pulse wave-based ultrasound manometry (PWUM)
- PMID: 21904023
- PMCID: PMC4005495
- DOI: 10.1088/0967-3334/32/10/012
Non-invasive measurement of local pulse pressure by pulse wave-based ultrasound manometry (PWUM)
Abstract
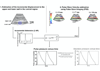
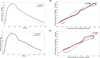
Central blood pressure (CBP) has been established as a relevant indicator of cardiovascular disease. Despite its significance, CBP remains particularly challenging to measure in standard clinical practice. The objective of this study is to introduce pulse wave-based ultrasound manometry (PWUM) as a simple-to-use, non-invasive ultrasound-based method for quantitative measurement of the central pulse pressure. Arterial wall displacements are estimated using radiofrequency ultrasound signals acquired at high frame rates and the pulse pressure waveform is estimated using both the distension waveform and the local pulse wave velocity. The method was tested on the abdominal aorta of 11 healthy subjects (age 35.7 ± 16 y.o.). PWUM pulse pressure measurements were compared to those obtained by radial applanation tonometry using a commercial system. The average intra-subject variability of the pulse pressure amplitude was found to be equal to 4.2 mmHg, demonstrating good reproducibility of the method. Excellent correlation was found between the waveforms obtained by PWUM and those obtained by tonometry in all subjects (0.94 < r < 0.98). A significant bias of 4.7 mmHg was found between PWUM and tonometry. PWUM is a highly translational method that can be easily integrated in clinical ultrasound imaging systems. It provides an estimate of the pulse pressure waveform at the imaged location, and may offer therefore the possibility to estimate the pulse pressure at different arterial sites. Future developments include the validation of the method against invasive estimates on patients, as well as its application to other large arteries.
Figures
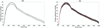

Similar articles
-
Noninvasive Evaluation of Varying Pulse Pressures in vivo Using Brachial Sphymomanometry, Applanation Tonometry, and Pulse Wave Ultrasound Manometry.Artery Res. 2017 Jun;18:22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.artres.2017.02.002. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Artery Res. 2017. PMID: 28989555 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-specific non-invasive estimation of the aortic blood pressure waveform by ultrasound and tonometry.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024 Apr;247:108082. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2024.108082. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38422893
-
[Comparison of central pulse pressure estimated from pulse wave propagation velocity and carotid pulse pressure measured by applantation tonometry].Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2002 Jul-Aug;95(7-8):637-40. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2002. PMID: 12365071 French.
-
Pulse wave analysis and pulse wave velocity: a critical review of their strengths and weaknesses.J Hypertens. 2003 Mar;21(3):463-72. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200303000-00004. J Hypertens. 2003. PMID: 12640232 Review.
-
[Pulse wave analysis: from the basic sciences to clinical applications].Przegl Lek. 2002;59 Suppl 3:9-14. Przegl Lek. 2002. PMID: 12652990 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
An inverse approach to determining spatially varying arterial compliance using ultrasound imaging.Phys Med Biol. 2016 Aug 7;61(15):5486-507. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/61/15/5486. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Phys Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27384105 Free PMC article.
-
Resonance sonomanometry for noninvasive, continuous monitoring of blood pressure.PNAS Nexus. 2024 Jul 30;3(7):pgae252. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae252. eCollection 2024 Jul. PNAS Nexus. 2024. PMID: 39081785 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-Impedance Sensor for Real-Time Artery Diameter Waveform Assessment.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Dec 17;21(24):8438. doi: 10.3390/s21248438. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34960542 Free PMC article.
-
Smartphone-based blood pressure monitoring via the oscillometric finger-pressing method.Sci Transl Med. 2018 Mar 7;10(431):eaap8674. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aap8674. Sci Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29515001 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mapping the longitudinal wall stiffness heterogeneities within intact canine aortas using Pulse Wave Imaging (PWI) ex vivo.J Biomech. 2013 Jul 26;46(11):1866-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 Jun 12. J Biomech. 2013. PMID: 23764176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization-International Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. Guidelines Subcommittee. J. Hypertens. 1999;17:151–183. - PubMed
-
- Avolio A, Van Bortel L, Boutouyrie P, Cockcroft J, McEniery C, Protogerou A, Roman M, Safar M, Segers P, Smulyan H. Role of pulse pressure amplification in arterial hypertension: Experts' opinion and review of the data. Hypertension. 2009;54:375–383. - PubMed
-
- Beulen BW, Bijnens N, Koutsouridis GG, Brands PJ, Rutten MC, van de Vosse FN. Toward noninvasive blood pressure assessment in artieries by using ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2011;37:788–797. - PubMed
-
- Brands PJ, Willigers JM, Ledoux LAF, Reneman RS, Hoeks APG. A noninvasive method to estimate pulse wave velocity in arteries locally by means of ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1998;24:1325–1335. - PubMed
-
- Chen C-H, Nevo E, Fetics B, Pak P, Yin F, Maughan W, Kass D. Estimation of Central aortic pressure waveform by mathematical transformation of radial tonometry pressure: Validation of generalized transfer function. Circulation. 1997;95:1827–1836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
