Gene Composer in a structural genomics environment
- PMID: 21904038
- PMCID: PMC3169390
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309111027424
Gene Composer in a structural genomics environment
Abstract
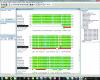
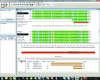
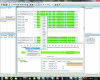
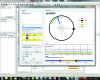
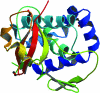
The structural genomics effort at the Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Disease (SSGCID) requires the manipulation of large numbers of amino-acid sequences and the underlying DNA sequences which are to be cloned into expression vectors. To improve efficiency in high-throughput protein structure determination, a database software package, Gene Composer, has been developed which facilitates the information-rich design of protein constructs and their underlying gene sequences. With its modular workflow design and numerous graphical user interfaces, Gene Composer enables researchers to perform all common bioinformatics steps used in modern structure-guided protein engineering and synthetic gene engineering. An example of the structure determination of H1N1 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase PB2 subunit is given.
Figures


References
-
- Chandonia, J. M. & Brenner, S. E. (2006). Science, 311, 347–351. - PubMed
-
- DeLano, W. L. (2002). PyMOL http://www.pymol.org.
-
- Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. (2004). Acta Cryst. D60, 2126–2132. - PubMed
-
- Gräslund, S., Sagemark, J., Berglund, H., Dahlgren, L. G., Flores, A., Hammarström, M., Johansson, I., Kotenyova, T., Nilsson, M., Nordlund, P. & Weigelt, J. (2008). Protein Expr. Purif. 58, 210–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

