Toward defining deficient emotional self-regulation in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder using the Child Behavior Checklist: a controlled study
- PMID: 21904086
- PMCID: PMC3737570
- DOI: 10.3810/pgm.2011.09.2459
Toward defining deficient emotional self-regulation in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder using the Child Behavior Checklist: a controlled study
Abstract
Objective: Deficient emotional self-regulation (DESR) is characterized by deficits in self-regulating the physiological arousal caused by strong emotions. We examined whether a unique profile of the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) would help identify DESR in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Methods: Subjects included 197 children with ADHD and 224 children without ADHD. We defined DESR if a child had an aggregate cut-off score of > 180 but < 210 on the Anxiety/Depression, Aggression, and Attention scales of the CBCL (CBCL-DESR). This profile was selected because of: 1) its conceptual congruence with the clinical concept of DESR; and 2) because its extreme (> 210) form has been previously associated with severe forms of mood and behavioral dysregulation in children with ADHD. All subjects were comprehensively assessed with structured diagnostic interviews and a wide range of functional measures.
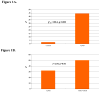
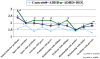
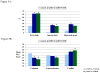
Results: Forty-four percent of children with ADHD had a positive CBCL-DESR profile versus 2% of controls (P < 0.001). The CBCL-DESR profile was associated with elevated rates of anxiety and disruptive behavior disorders, as well as significantly more impairments in emotional and interpersonal functioning.
Conclusions: The CBCL-DESR profile helped identify a subgroup of children with ADHD who had a psychopathological and functional profile consistent with the clinical concept of DESR.
Figures



References
-
- Barkley RA. Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention, and executive functions: constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychol Bull. 1997;121(1):65–94. - PubMed
-
- Barkley RA. Deficient Emotional Self-Regulation: A Core Component of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Journal of ADHD and Related Disorders. 2010;1(2):5–37.
-
- Surman CBH, Biederman J, Spencer TJ, Miller CA, Faraone SV. Understanding Deficient Emotional Self Regulation in Adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Controlled Study. American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting; New York. 2010.
-
- Reimherr FW, Marchant BK, Williams ED, Strong RE, Halls C, Soni P. Personality disorders in ADHD Part 3: Personality disorder, social adjustment, and their relation to dimensions of adult ADHD. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2010;22(2):103–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
