Effect of exposure of human monocyte-derived macrophages to high, versus normal, glucose on subsequent lipid accumulation from glycated and acetylated low-density lipoproteins
- PMID: 21904540
- PMCID: PMC3166758
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/851280
Effect of exposure of human monocyte-derived macrophages to high, versus normal, glucose on subsequent lipid accumulation from glycated and acetylated low-density lipoproteins
Abstract
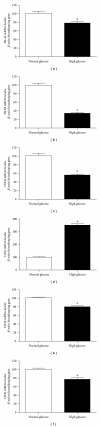
During atherosclerosis monocyte-derived macrophages accumulate cholesteryl esters from low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) via lectin-like oxidised LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1) and class AI and AII (SR-AI, SR-AII) and class B (SR-BI, CD36) scavenger receptors. Here we examined the hypothesis that hyperglycaemia may modulate receptor expression and hence lipid accumulation in macrophages. Human monocytes were matured into macrophages in 30 versus 5 mM glucose and receptor expression and lipid accumulation quantified. High glucose elevated LOX1 mRNA, but decreased SR-AI, SR-BI, LDLR, and CD36 mRNA. SR-BI and CD36 protein levels were decreased. Normo- and hyperglycaemic cells accumulated cholesteryl esters from modified LDL to a greater extent than control LDL, but total and individual cholesteryl ester accumulation was not affected by glucose levels. It is concluded that, whilst macrophage scavenger receptor mRNA and protein levels can be modulated by high glucose, these are not key factors in lipid accumulation by human macrophages under the conditions examined.
Figures

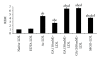


References
-
- World Health Organisation. Diabetes. Fact Sheet No. 312, 2006.
-
- Jenkins AJ, Best JD, Klein RL, Lyons TJ. Lipoproteins, glycoxidation and diabetic angiopathy. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews. 2004;20(5):349–368. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 2001;414(6865):813–820. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed N. Advanced glycation endproducts—role in pathology of diabetic complications. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2005;67(1):3–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
