Electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry of sodiated adducts of cholesteryl esters
- PMID: 21904795
- PMCID: PMC3215890
- DOI: 10.1007/s11745-011-3609-2
Electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry of sodiated adducts of cholesteryl esters
Abstract
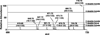
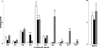
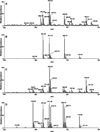
Cholesteryl esters (CE) are important lipid storage molecules. The present study demonstrates that sodiated adducts of CE molecular species form positive ions that can be detected in both survey scan mode as well as by exploiting class-specific fragmentation in MS/MS scan modes. A common neutral loss for CE is the loss of cholestane (NL 368.5), which can be used to specifically quantify tissue CE molecular species. Using this MS/MS technique, CE molecular species were quantified in mouse monocyte-derived macrophages (J774 cells) incubated with either linoleic (18:2) or arachidonic acid (20:4). These studies revealed that arachidonic acid was not only incorporated into the CE pool, but also was elongated resulting in the accumulation of 22:4 and 24:4 CE molecular species in macrophages. Additionally, this technique was used to quantify CE molecular species present in crude lipid extracts from plasma of female mice fed a Western diet, which led to an enrichment in CE molecular species containing monounsaturated fatty acids compared to female mice fed a normal chow diet. Last, NL 368.5 spectra revealed the oxidation of the aliphatic fatty acid residues of CE molecular species containing polyunsaturated fatty acids. Taken together, these studies demonstrate the utility of using sodiated adducts of CE in conjunction with direct infusion electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry to rapidly quantify CE molecular species in biological samples.
Figures





References
-
- Brown MS, Ho YK, Goldstein JL. The cholesteryl ester cycle in macrophage foam cells. Continual hydrolysis and re-esterification of cytoplasmic cholesteryl esters. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:9344–9352. - PubMed
-
- Meng X, Zou D, Shi Z, Duan Z, Mao Z. Dietary diacylglycerol prevents high-fat Diet-induced lipid accumulation in rat liver and abdominal adipose tissue. Lipids. 2004;39:37–41. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz CC, VandenBroek JM, Cooper PS. Lipoprotein cholesteryl ester production, transfer, and output in vivo in humans. J. Lipid Res. 2004;45:1594–1607. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. The SREBP Pathway: Regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 1997;89:331–340. - PubMed
-
- Francone OL, Gurakar A, Fielding C. Distribution and functions of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and cholesteryl ester transfer protein in plasma lipoproteins. Evidence for a functional unit containing these activities together with apolipoproteins A–I and D that catalyzes the esterification and transfer of cell-derived cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:7066–7072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

