Exploiting bacterial DNA gyrase as a drug target: current state and perspectives
- PMID: 21904817
- PMCID: PMC3189412
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-011-3557-z
Exploiting bacterial DNA gyrase as a drug target: current state and perspectives
Abstract
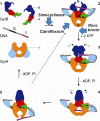
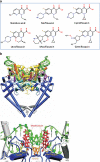
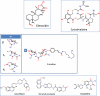
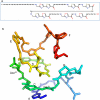
DNA gyrase is a type II topoisomerase that can introduce negative supercoils into DNA at the expense of ATP hydrolysis. It is essential in all bacteria but absent from higher eukaryotes, making it an attractive target for antibacterials. The fluoroquinolones are examples of very successful gyrase-targeted drugs, but the rise in bacterial resistance to these agents means that we not only need to seek new compounds, but also new modes of inhibition of this enzyme. We review known gyrase-specific drugs and toxins and assess the prospects for developing new antibacterials targeted to this enzyme.
Figures


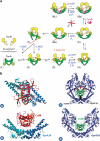

References
-
- Andersen NR, Rasmussen PR. The constitution of clerocidin a new antibiotic isolated from Oidiodendron truncatum. Tetrahedron Letters. 1984;25(4):465–468. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)99912-X. - DOI
-
- Angehrn P, Buchmann S, Funk C, Goetschi E, Gmuender H, Hebeisen P, Kostrewa D, Link H, Luebbers T, Masciadri R, Nielsen J, Reindl P, Ricklin F, Schmitt-Hoffmann A, Theil FP. New antibacterial agents derived from the DNA gyrase inhibitor cyclothialidine. J Med Chem. 2004;47(6):1487–1513. doi: 10.1021/jm0310232. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

