Distinct functional and conformational states of the human lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase catalytic domain can be targeted by choice of the inhibitor chemotype
- PMID: 21904909
- PMCID: PMC8118164
- DOI: 10.1007/s10822-011-9469-2
Distinct functional and conformational states of the human lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase catalytic domain can be targeted by choice of the inhibitor chemotype
Abstract
The lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase (LYP), encoded by the PTPN22 gene, has recently been identified as a promising drug target for human autoimmunity diseases. Like the majority of protein-tyrosine phosphatases LYP can adopt two functionally distinct forms determined by the conformation of the WPD-loop. The WPD-loop plays an important role in the catalytic dephosphorylation by protein-tyrosine phosphatases. Here we investigate the binding modes of two chemotypes of small molecule LYP inhibitors with respect to both protein conformations using computational modeling. To evaluate binding in the active form, we built a LYP protein structure model of high quality. Our results suggest that the two different compound classes investigated, bind to different conformations of the LYP phosphatase domain. Binding to the closed form is facilitated by an interaction with Asp195 in the WPD-loop, presumably stabilizing the active conformation. The analysis presented here is relevant for the design of inhibitors that specifically target either the closed or the open conformation of LYP in order to achieve better selectivity over phosphatases with similar binding sites.
© Springer Science+Business Media B.V. 2011
Figures


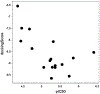
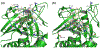


References
-
- Hunter T (2000) Signaling—2000 and beyond. Cell 100(1):113–127 - PubMed
-
- Tonks NK (1993) Introduction: protein tyrosine phosphatases. Semin Cell Biol 4(6):373–377 - PubMed
-
- Zhang ZY (1998) Protein-tyrosine phosphatases: biological function, structural characteristics, and mechanism of catalysis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 33(1):1–52 - PubMed
-
- Cohen P (2002) Protein kinases—the major drug targets of the twenty-first century? Nat Rev Drug Discov 1(4):309–315 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

