Rib fracture as a predictor of future fractures in young and older postmenopausal women: National Osteoporosis Risk Assessment (NORA)
- PMID: 21904951
- PMCID: PMC3640849
- DOI: 10.1007/s00198-011-1757-0
Rib fracture as a predictor of future fractures in young and older postmenopausal women: National Osteoporosis Risk Assessment (NORA)
Abstract
A rib fracture history after age 45 was associated with a 5.4-fold increase in new rib fracture risk and a 2.4-fold increase in risk of any new clinical fracture in 155,031 postmenopausal women. A rib fracture history suggests osteoporosis and should be considered when evaluating patients for interventions to prevent fractures.
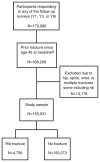
Introduction: Until recently, little attention was paid to rib fracture as an osteoporosis marker. Emerging evidence suggests rib fracture may be an osteoporotic fracture in men and women. We report the 5-year independent association between baseline rib fracture histories and self-reported future fractures by age (decade) in the NORA cohort (155,031 postmenopausal women, 50-99 years).
Methods: Participants reported fracture history and responded to follow-up surveys at years 1, 3, or 6. Women with a baseline rib fracture history without other fractures were compared with women with no fracture.
Results: At baseline, 4,758 (3.07%) women reported a rib fracture history without other fractures; 6,300 women reported 6,830 new clinical fractures, including wrist (2,271), rib (1,891), spine (1,136), hip (941), and forearm (591). Adjusted relative risk (ARR) values (95% confidence interval [CI]) for future fractures in women with rib fracture history versus women with no fracture history were 5.4 (4.8-6.1) at the rib, 2.1 (1.7-2.6) at the spine, and 1.4 (1.1-1.7) at the wrist, and not significant for forearm or hip fractures. Future fracture risk was at least doubled in women with a rib fracture history in all ages: ARR (95% CI) 3.4 (2.8-4.0) for ages 50-59, 2.5 (2.1-3.0) for ages 60-69, 2.0 (1.7-2.3) for ages 70-79, and 2.0 (1.6-2.6) for ages >80.
Conclusions: Rib fracture, the second most common clinical fracture in women (after wrist fracture), predicted future fractures of the rib, wrist, and spine at all ages. Women presenting with rib fractures should be evaluated for appropriate management to prevent future fractures.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
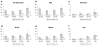
References
-
- Melton LJ, 3rd, Chrischilles EA, Cooper C, Lane AW, Riggs BL. Perspective. How many women have osteoporosis? J Bone Miner Res. 1992;7:1005–1010. - PubMed
-
- Klotzbuecher CM, Ross PD, Landsman PB, Abbott TA, 3rd, Berger M. Patients with prior fractures have an increased risk of future fractures: a summary of the literature and statistical synthesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15:721–739. - PubMed
-
- Kanis JA, Johnell O, De Laet C, et al. A meta-analysis of previous fracture and subsequent fracture risk. Bone. 2004;35:375–382. - PubMed
-
- Porthouse J, Birks YF, Torgerson DJ, Cockayne S, Puffer S, Watt I. Risk factors for fracture in a UK population: a prospective cohort study. Q J Med. 2004;97:569–574. - PubMed
-
- Mallmin H, Ljunghall S, Persson I, Naessen T, Krusemo UB, Bergstrom R. Fracture of the distal forearm as a forecaster of subsequent hip fracture: a population-based cohort study with 24 years of follow-up. Calcif Tissue Int. 1993;52:269–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 AR45632/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45647/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45614/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK031801/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG027810/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG007181/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045632/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045614/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45654/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG007181/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045654/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG07181/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045647/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45580/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG027810/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045580/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG18197/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG018197/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG028507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

