Noncardiac vascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis: increase in venous thromboembolic events?
- PMID: 21905005
- PMCID: PMC3474372
- DOI: 10.1002/art.33322
Noncardiac vascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis: increase in venous thromboembolic events?
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the incidence of noncardiac vascular disease in a community-based incidence cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and compare it to that in the general population and to investigate trends in the incidence of noncardiac vascular disease in patients with RA.
Methods: A population-based inception cohort of patients with incident RA between January 1, 1980 and December 31, 2007 in Olmsted County, Minnesota and a cohort of non-RA subjects from the same population base was assembled and followed up until December 31, 2008. Venous thromboembolic, cerebrovascular, and peripheral arterial events were ascertained by medical record review.
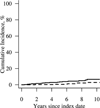
Results: The study population included 813 patients with RA with a mean±SD age of 55.9±15.7 years (68% women) and an average length of followup of 9.6±6.9 years. Compared to non-RA subjects of similar age and sex, patients diagnosed as having RA between 1995 and 2007 had a higher incidence (%) of venous thromboembolism (cumulative incidence±SE 6.7±1.7 versus 2.8±1.1, respectively; P=0.005) but similar rates of cerebrovascular and peripheral arterial events. Among patients with RA, the incidence of venous thromboembolic, cerebrovascular, and peripheral arterial events was similar in the 1995-2007 time period compared to the 1980-1994 time period.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that the incidence of venous thromboembolism is increased in patients with RA compared to non-RA subjects. The incidence of cerebrovascular events and peripheral vascular disease events is similar in patients with RA compared to non-RA subjects. Among patients with RA, the incidence of noncardiac vascular disease has remained stable in recent decades.
Copyright © 2012 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Maradit-Kremers H, Crowson CS, Nicola PJ, Ballman KV, Roger VL, Jacobsen SJ, et al. Increased unrecognized coronary heart disease and sudden deaths in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(2):402–411. - PubMed
-
- Nicola PJ, Maradit-Kremers H, Roger VL, Jacobsen SJ, Crowson CS, Ballman KV, et al. The risk of congestive heart failure in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study over 46 years. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(2):412–420. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez A, Maradit Kremers H, Crowson CS, Nicola PJ, Davis JM, 3rd, Therneau TM, et al. The widening mortality gap between rheumatoid arthritis patients and the general population. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(11):3583–3587. - PubMed
-
- Matta F, Singala R, Yaekoub AY, Najjar R, Stein PD. Risk of venous thromboembolism with rheumatoid arthritis. Thromb Haemost. 2009;101(1):134–138. - PubMed
-
- Kawakami K, Ikari K, Kawamura K, Tsukahara S, Iwamoto T, Yano K, et al. Complications and features after joint surgery in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with tumour necrosis factor-alpha blockers: perioperative interruption of tumour necrosis factor-alpha blockers decreases complications? Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010;49(2):341–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical