Increased betulinic acid induced cytotoxicity and radiosensitivity in glioma cells under hypoxic conditions
- PMID: 21906280
- PMCID: PMC3182903
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-111
Increased betulinic acid induced cytotoxicity and radiosensitivity in glioma cells under hypoxic conditions
Abstract
Background: Betulinic acid (BA) is a novel antineoplastic agent under evaluation for tumor therapy. Because of the selective cytotoxic effects of BA in tumor cells (including gliomas), the combination of this agent with conservative therapies (such as radiotherapy and chemotherapy) may be useful. Previously, the combination of BA with irradiation under hypoxic conditions had never been studied.
Methods: In this study, the effects of 3 to 30 μM BA on cytotoxicity, migration, the protein expression of PARP, survivin and HIF-1α, as well as radiosensitivity under normoxic and hypoxic conditions were analyzed in the human malignant glioma cell lines U251MG and U343MG. Cytotoxicity and radiosensitivity were analyzed with clonogenic survival assays, migration was analyzed with Boyden chamber assays (or scratch assays) and protein expression was examined with Western blot analyses.
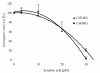
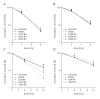
Results: Under normoxic conditions, a half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 23 μM was observed in U251MG cells and 24 μM was observed in U343MG cells. Under hypoxic conditions, 10 μM or 15 μM of BA showed a significantly increased cytotoxicity in U251MG cells (p = 0.004 and p = 0.01, respectively) and U343MG cells (p < 0.05 and p = 0.01, respectively). The combination of BA with radiotherapy resulted in an additive effect in the U343MG cell line under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Weak radiation enhancement was observed in U251MG cell line after treatment with BA under normoxic conditions. Furthermore, under hypoxic conditions, the incubation with BA resulted in increased radiation enhancement. The enhancement factor, at an irradiation dose of 15 Gy after treatment with 10 or 15 μM BA, was 2.20 (p = 0.02) and 4.50 (p = 0.03), respectively. Incubation with BA led to decreased cell migration, cleavage of PARP and decreased expression levels of survivin in both cell lines. Additionally, BA treatment resulted in a reduction of HIF-1α protein under hypoxic conditions.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that BA is capable of improving the effects of tumor therapy in human malignant glioma cells, particularly under hypoxic conditions. Further investigations are necessary to characterize its potential as a radiosensitizer.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Betulinic acid derivatives NVX-207 and B10 for treatment of glioblastoma--an in vitro study of cytotoxicity and radiosensitization.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Oct 30;15(11):19777-90. doi: 10.3390/ijms151119777. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25361208 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1α inhibition by siRNA or chetomin in human malignant glioma cells: effects on hypoxic radioresistance and monitoring via CA9 expression.BMC Cancer. 2010 Nov 4;10:605. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-605. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21050481 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Betulinic Acid-Cisplatin conjugate APC and its precursor DE9B for the treatment of human malignant glioma.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Dec 1;314:108841. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108841. Epub 2019 Oct 2. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 31586452
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the potential of betulinic acid in cancer prevention and treatment.Phytomedicine. 2024 Sep;132:155858. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155858. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39053249 Review.
-
Targeting tumor hypoxia and mitochondrial metabolism with anti-parasitic drugs to improve radiation response in high-grade gliomas.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 7;39(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01724-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33028364 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural radioprotectors and their impact on cancer drug discovery.Radiat Oncol J. 2018 Dec;36(4):265-275. doi: 10.3857/roj.2018.00381. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Radiat Oncol J. 2018. PMID: 30630265 Free PMC article.
-
Betulinic acid derivatives NVX-207 and B10 for treatment of glioblastoma--an in vitro study of cytotoxicity and radiosensitization.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Oct 30;15(11):19777-90. doi: 10.3390/ijms151119777. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25361208 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches to improve the oral bioavailability and effects of novel anticancer drugs berberine and betulinic acid.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 10;9(3):e89919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089919. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24614362 Free PMC article.
-
Betulin Sulfonamides as Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors and Anticancer Agents in Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 16;22(16):8808. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168808. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445506 Free PMC article.
-
South Asian Medicinal Compounds as Modulators of Resistance to Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2016 Mar 5;8(3):32. doi: 10.3390/cancers8030032. Cancers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26959063 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eiznhamer DA, Xu ZQ. Betulinic acid: a promising anticancer candidate. IDrugs. 2004;7:(4): 359–373. - PubMed
-
- Pisha E, Chai H, Lee IS, Chagwedera TE, arnsworth NR, Cordell GA, Beecher CW, Fong HH, Kinghorn AD, Brown DM. et al.Discovery of betulinic acid as a selective inhibitor of human melanoma that functions by induction of apoptosis. Nat Med. 1995;1(10):1046–1051. doi: 10.1038/nm1095-1046. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

