Upstream molecular signaling pathways of p27(Kip1) expression in human breast cancer cells in vitro: differential effects of 4-hydroxytamoxifen and deficiency of either D-(+)-glucose or L-leucine
- PMID: 21906315
- PMCID: PMC3180262
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-11-31
Upstream molecular signaling pathways of p27(Kip1) expression in human breast cancer cells in vitro: differential effects of 4-hydroxytamoxifen and deficiency of either D-(+)-glucose or L-leucine
Abstract
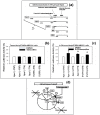
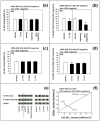
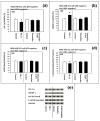
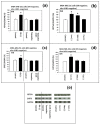
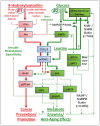
Background: The objective of this study was to investigate whether the levels of glucose or certain amino acids could regulate the expression of a cell cycle repressor protein p27(Kip1), thereby dictating the risk of cancer in either obesity or caloric/dietary restriction. Previously, we identified and reported four different upstream molecular signaling pathways of p27 expression in human breast cancer cells. We called these four pathways as pathway #1, #2, #3 and #4. We found that 4-hydroxytamoxifen - but not tamoxifen - up-regulated the expression of p27 using pathway #1 which consisted mainly of receptor tyrosine kinases and mTORC1. We now investigate, using 4-hydroxytamoxifen as a reference anti-cancer agents, whether (a) the moderate increase in the concentration of D-(+)-glucose could down-regulate and, conversely, (b) the deficiency of D-(+)-glucose or certain L-amino acids could up-regulate the expression of p27 in these cells using pathway #2 which consists mainly of AMPK and mTORC1.
Results: Using human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in vitro, these hypotheses were tested experimentally by performing p27-luciferase reporter transfection assays and western immunoblot analyses. The results obtained are consistent with these hypotheses. Furthermore, the results indicated that, although 4-hydroxytamoxifen used primarily pathway #1 to down-regulate the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and up-regulate the expression of p27, it also secondarily down-regulated the phosphorylation of S6K1. In contrast, the deficiency of D-(+)-glucose or L-leucine used primarily pathway #2 to down-regulate the phosphorylation of S6K1, but they also secondarily down-regulated the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and up-regulated the expression of p27. Finally, deficiency of D-(+)-glucose or L-leucine - but not 4-hydroxytamoxifen - up-regulated the expression of mitochondrial ATP5A and SIRT3.
Conclusions: (a) 4-Hydroxitamoxifen used primarily pathway #1 to up-regulate the expression of p27. (b) Moderate increase in the concentration of D-(+)-glucose used primarily pathway #2 to down-regulate the expression of p27. (c) Deficiency of D-(+)-glucose or L-leucine also used primarily pathway #2 to up-regulate the expression of p27. (d) Deficiency of D-(+)-glucose or L-leucine - but not 4-hydroxytamoxifen - up-regulated the expression of mitochondrial ATP5A in the Complex V of respiratory oxidation-phosphorylation chain and mitochondrial SIRT3. The SIRT3 is one of the seven mammalian anti-aging as well as anti-metabolic sirtuins.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of p27Kip1, a cell cycle repressor protein, is inversely associated with potential carcinogenic risk in the genetic rodent models of obesity and long-lived Ames dwarf mice.Metabolism. 2013 Jun;62(6):873-87. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.01.001. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23357529 Free PMC article.
-
Upstream molecular signaling pathways of p27(Kip1) expression: effects of 4-hydroxytamoxifen, dexamethasone, and retinoic acids.Cancer Cell Int. 2010 Feb 19;10:3. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-10-3. Cancer Cell Int. 2010. PMID: 20170512 Free PMC article.
-
"Nutritional and chemopreventive anti-cancer agents up-regulate expression of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in mouse JB6 epidermal and human MCF7, MDA-MB-321 and AU565 breast cancer cells".Cancer Cell Int. 2006 Aug 9;6:20. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-6-20. Cancer Cell Int. 2006. PMID: 16899133 Free PMC article.
-
BCR signals target p27(Kip1) and cyclin D2 via the PI3-K signalling pathway to mediate cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of WEHI 231 B cells.Oncogene. 2001 Nov 1;20(50):7352-67. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204951. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11704865
-
The AMPK/p27Kip1 Pathway as a Novel Target to Promote Autophagy and Resilience in Aged Cells.Cells. 2021 Jun 8;10(6):1430. doi: 10.3390/cells10061430. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34201101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glibenclamide inhibits cell growth by inducing G0/G1 arrest in the human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013 Jan 11;14:6. doi: 10.1186/2050-6511-14-6. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23311706 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of autophagy by glucose in Mammalian cells.Cells. 2012 Jul 27;1(3):372-95. doi: 10.3390/cells1030372. Cells. 2012. PMID: 24710481 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting SIRT2 in Aging-Associated Fibrosis Pathophysiology.Aging Dis. 2024 Jul 5;16(4):2036-2053. doi: 10.14336/AD.202.0513. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 39226168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of p27Kip1, a cell cycle repressor protein, is inversely associated with potential carcinogenic risk in the genetic rodent models of obesity and long-lived Ames dwarf mice.Metabolism. 2013 Jun;62(6):873-87. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.01.001. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23357529 Free PMC article.
-
ATP5A1 and ATP5B are highly expressed in glioblastoma tumor cells and endothelial cells of microvascular proliferation.J Neurooncol. 2016 Feb;126(3):405-13. doi: 10.1007/s11060-015-1984-x. Epub 2015 Nov 2. J Neurooncol. 2016. PMID: 26526033
References
-
- Eto I. G1 cell cycle regulatory proteins in chemically induced rat mammary adenocarcinomas in vivo and tumor promotion-sensitive, -resistant, and transformed mouse epidermal cells in vitro. Cell Cycle. 2003;2:149–156. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

