Arg kinase regulates epithelial cell polarity by targeting β1-integrin and small GTPase pathways
- PMID: 21906945
- PMCID: PMC3189484
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.08.023
Arg kinase regulates epithelial cell polarity by targeting β1-integrin and small GTPase pathways
Abstract
Background: Establishment and maintenance of epithelial cell polarity is regulated in part by signaling from adhesion receptors. Loss of cell polarity is associated with multiple pathologies including the initiation and progression of various cancers. The β1-integrin adhesion receptor plays a role in the regulation of cell polarity; however, the identity of the signaling pathways that modulate β1-integrin function and connect it to the regulation of polarity pathways remains largely unknown.
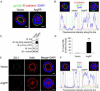
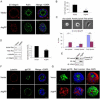
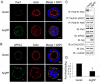
Results: The present work identifies a role for Arg, a member of the Abl family nonreceptor tyrosine kinases, in the regulation of adhesive signals and epithelial cell polarity. In a three-dimensional cell culture model, activation of Arg kinase leads to a striking inversion of apical-basal polarity. In contrast, loss of Arg function impairs the establishment of a polarized epithelial cyst structure. Activated Arg kinase disrupts β1-integrin signaling and localization and impairs Rac1-mediated laminin assembly. Disruption of β1-integrin function by active Arg results in altered distribution of selected polarity complex components mediated in part by Rap1 GTPase signaling. Whereas polarity inversion is partially rescued by a constitutively active Rap1, Rac1-dependent laminin assembly is not, indicating that Rap1 and Rac1 signal independently during epithelial polarity.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that modulation of Arg kinase function may contribute not only to normal epithelial polarity regulation but also may promote pathologies associated with loss of cell polarity.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

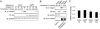

Similar articles
-
Breast cancer cell migration is regulated through junctional adhesion molecule-A-mediated activation of Rap1 GTPase.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Mar 23;13(2):R31. doi: 10.1186/bcr2853. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21429211 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial Membrane Protein 2 and β1 integrin signaling regulate APC-mediated processes.Exp Cell Res. 2017 Jan 1;350(1):190-198. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.11.021. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 27890644
-
Junctional adhesion molecule A interacts with Afadin and PDZ-GEF2 to activate Rap1A, regulate beta1 integrin levels, and enhance cell migration.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Apr;20(7):1916-25. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-10-1014. Epub 2009 Jan 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19176753 Free PMC article.
-
Junctional adhesion molecule 1 regulates epithelial cell morphology through effects on beta1 integrins and Rap1 activity.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 25;280(12):11665-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412650200. Epub 2005 Jan 27. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15677455
-
Activated R-ras, Rac1, PI 3-kinase and PKCepsilon can each restore cell spreading inhibited by isolated integrin beta1 cytoplasmic domains.J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1549-60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1549. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11134082 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Abl2 is recruited to ventral actin waves through cytoskeletal interactions to promote lamellipodium extension.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Nov 15;29(23):2863-2873. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-01-0044. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30256707 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the ABL tyrosine kinases in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the metastatic cascade.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 May 22;19(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00739-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34022881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of different components in the peritumoral tissue microenvironment of colorectal cancer: A potential prospect in tumorigenesis.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Sep;14(3):2555-65. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5584. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27484148 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of Arg/Abl2 improves endothelial cell adhesion and prevents vascular leak during inflammation.Angiogenesis. 2021 Aug;24(3):677-693. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09781-x. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Angiogenesis. 2021. PMID: 33770321 Free PMC article.
-
Polarity in mammalian epithelial morphogenesis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Feb 1;5(2):a013789. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013789. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23378592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tanos B, Rodriguez-Boulan E. The epithelial polarity program: machineries involved and their hijacking by cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:6939–6957. - PubMed
-
- Lee M, Vasioukhin V. Cell polarity and cancer--cell and tissue polarity as a non-canonical tumor suppressor. Journal of cell science. 2008;121:1141–1150. - PubMed
-
- White DE, Kurpios NA, Zuo D, Hassell JA, Blaess S, Mueller U, Muller WJ. Targeted disruption of beta1-integrin in a transgenic mouse model of human breast cancer reveals an essential role in mammary tumor induction. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:159–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

