Choreography of bacteriophage T7 DNA replication
- PMID: 21907611
- PMCID: PMC3195405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.07.024
Choreography of bacteriophage T7 DNA replication
Abstract
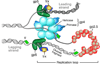
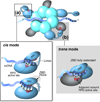
The replication system of phage T7 provides a model for DNA replication. Biochemical, structural, and single-molecule analyses together provide insight into replisome mechanics. A complex of polymerase, a processivity factor, and helicase mediates leading strand synthesis. Establishment of the complex requires an interaction of the C-terminal tail of the helicase with the polymerase. During synthesis the complex is stabilized by other interactions to provide for a processivity of 5 kilobase (kb). The C-terminal tail also interacts with a distinct region of the polymerase to captures dissociating polymerase to increase the processivity to >17kb. The lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously within a loop that forms and resolves during each cycle of Okazaki fragment synthesis. The synthesis of a primer as well as the termination of a fragment signal loop resolution.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Richardson CC. Bacteriophage T7: minimal requirements for the replication of a duplex DNA molecule. Cell. 1983;33:315–317. - PubMed
-
-
Hamdan SM, Richardson CC. Motors, switches, and contacts in the replisome. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:205–243. This review provides a comprehensive description on the interactions that occur during DNA replication with emphasis on the bacteriophage T7 system. Principles governing interactions between components of the replisome and mechanisms for coordinated synthesis of leading and lagging strands are broadly discussed.
-
-
- Lee J, Chastain PD, 2nd, Kusakabe T, Griffith JD, Richardson CC. Coordinated leading and lagging strand DNA synthesis on a minicircular template. Mol Cell. 1998;1:1001–1010. - PubMed
-
- Doublie S, Tabor S, Long AM, Richardson CC, Ellenberger T. Crystal structure of a bacteriophage T7 DNA replication complex at 2.2 A resolution. Nature. 1998;391:251–258. - PubMed
-
- Singleton MR, Sawaya MR, Ellenberger T, Wigley DB. Crystal structure of T7 gene 4 ring helicase indicates a mechanism for sequential hydrolysis of nucleotides. Cell. 2000;101:589–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

