NF-κB regulates DNA double-strand break repair in conjunction with BRCA1-CtIP complexes
- PMID: 21908405
- PMCID: PMC3245919
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr687
NF-κB regulates DNA double-strand break repair in conjunction with BRCA1-CtIP complexes
Abstract
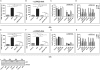
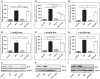
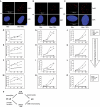
NF-κB is involved in immune responses, inflammation, oncogenesis, cell proliferation and apoptosis. Even though NF-κB can be activated by DNA damage via Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated (ATM) signalling, little was known about an involvement in DNA repair. In this work, we dissected distinct DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair mechanisms revealing a stimulatory role of NF-κB in homologous recombination (HR). This effect was independent of chromatin context, cell cycle distribution or cross-talk with p53. It was not mediated by the transcriptional NF-κB targets Bcl2, BAX or Ku70, known for their dual roles in apoptosis and DSB repair. A contribution by Bcl-xL was abrogated when caspases were inhibited. Notably, HR induction by NF-κB required the targets ATM and BRCA2. Additionally, we provide evidence that NF-κB interacts with CtIP-BRCA1 complexes and promotes BRCA1 stabilization, and thereby contributes to HR induction. Immunofluorescence analysis revealed accelerated formation of replication protein A (RPA) and Rad51 foci upon NF-κB activation indicating HR stimulation through DSB resection by the interacting CtIP-BRCA1 complex and Rad51 filament formation. Taken together, these results define multiple NF-κB-dependent mechanisms regulating HR induction, and thereby providing a novel intriguing explanation for both NF-κB-mediated resistance to chemo- and radiotherapies as well as for the sensitization by pharmaceutical intervention of NF-κB activation.
Figures




References
-
- Perkins ND. Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-κB and IKK function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:49–62. - PubMed
-
- Habraken Y, Piette J. NF-kappaB activation by double-strand breaks. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006;72:1132–1141. - PubMed
-
- Stilmann M, Hinz M, Arslan SC, Zimmer A, Schreiber V, Scheidereit C. A nuclear poly(ADP-Ribose)-dependent signalosome confers DNA damage-induced IκB kinase activation. Mol. Cell. 2009;36:365–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

