Nicotine, carbon monoxide, and carcinogen exposure after a single use of a water pipe
- PMID: 21908725
- PMCID: PMC3210932
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-0545
Nicotine, carbon monoxide, and carcinogen exposure after a single use of a water pipe
Abstract
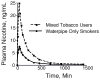
Background: Smoking tobacco preparations in a water pipe (hookah) is widespread in many places of the world, including the United States, where it is especially popular among young people. Many perceive water pipe smoking to be less hazardous than cigarette smoking. We studied systemic absorption of nicotine, carbon monoxide, and carcinogens from one water pipe smoking session.
Methods: Sixteen subjects smoked a water pipe on a clinical research ward. Expired carbon monoxide and carboxyhemoglobin were measured, plasma samples were analyzed for nicotine concentrations, and urine samples were analyzed for the tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) metabolite biomarker concentrations.
Results: We found substantial increases in plasma nicotine concentrations, comparable to cigarette smoking, and increases in carbon monoxide levels that are much higher than those typically observed from cigarette smoking, as previously published. Urinary excretion of NNAL and PAH biomarkers increased significantly following water pipe smoking.
Conclusions: Absorption of nicotine in amounts comparable to cigarette smoking indicates a potential for addiction, and absorption of significant amounts of carcinogens raise concerns of cancer risk in people who smoke tobacco products in water pipes.
Impact: Our data contribute to an understanding of the health impact of water pipe use.
© 2011 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Benowitz is a consultant to several pharmaceutical companies that market medications to aid smoking cessation and has served as a paid expert witness in litigation against tobacco companies. The other authors have no conflicts to declare.
Figures



References
-
- WHO Study Group on Tobacco Product Regulation [TobReg] TobReg - Advisory Note Waterpipe Tobacco Smoking: Health Effects, Research Needs and Recommended Actions by Regulators. Geneva: Switzerland.: World Health Organization; 2005.
-
- Hadidi KA, Mohammed FI. Nicotine content in tobacco used in hubble-bubble smoking. Saudi Med J. 2004;25:912–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

