Exactly the same but different: promiscuity and diversity in the molecular mechanisms of action of the aryl hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptor
- PMID: 21908767
- PMCID: PMC3196658
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr218
Exactly the same but different: promiscuity and diversity in the molecular mechanisms of action of the aryl hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptor
Abstract
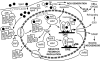
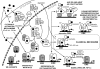
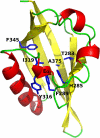
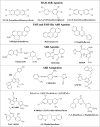
The Ah receptor (AhR) is a ligand-dependent transcription factor that mediates a wide range of biological and toxicological effects that result from exposure to a structurally diverse variety of synthetic and naturally occurring chemicals. Although the overall mechanism of action of the AhR has been extensively studied and involves a classical nuclear receptor mechanism of action (i.e., ligand-dependent nuclear localization, protein heterodimerization, binding of liganded receptor as a protein complex to its specific DNA recognition sequence and activation of gene expression), details of the exact molecular events that result in most AhR-dependent biochemical, physiological, and toxicological effects are generally lacking. Ongoing research efforts continue to describe an ever-expanding list of ligand-, species-, and tissue-specific spectrum of AhR-dependent biological and toxicological effects that seemingly add even more complexity to the mechanism. However, at the same time, these studies are also identifying and characterizing new pathways and molecular mechanisms by which the AhR exerts its actions and plays key modulatory roles in both endogenous developmental and physiological pathways and response to exogenous chemicals. Here we provide an overview of the classical and nonclassical mechanisms that can contribute to the differential sensitivity and diversity in responses observed in humans and other species following ligand-dependent activation of the AhR signal transduction pathway.
Figures
References
-
- Aarts JMMJG, Denison MS, Cox MA, Schalk MA, Garrison PM, Tullis K, de Haan LH, Brouwer A. Species-specific antagonism of Ah receptor action by 2,2',5,5'-tetrachloro- and 2,2',3,3',4,4'-hexachlorobiphenyl. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996;293:463–474. - PubMed
-
- Abdelrahim M, Ariazi E, Kim K, Khan S, Barhoumi R, Burghardt R, Liu S, Hill D, Finnell R, Wlodarczyk B, et al. 3-Methylcholanthrene and other aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists directly activate estrogen receptor alpha. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2459–2467. - PubMed
-
- Abdelrahim M, Smith R, III, Safe S. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor gene silencing with small inhibitory RNA differentially modulates Ah-responsiveness in MCF-7 and HepG2 cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003;63:1373–1381. - PubMed
-
- Abel J, Haarmann-Stemmann T. An introduction to the molecular basics of aryl hydrocarbon receptor biology. Biol. Chem. 2010;391:1235–1248. - PubMed
-
- Abnet CC, Tanguay RL, Heideman W, Peterson RE. Transactivation activity of human, zebrafish, and rainbow trout aryl hydrocarbon receptors expressed in COS-7 cells: greater insight into species differences in toxic potency of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin, dibenzofuran, and biphenyl congeners. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1999;159:41–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

