LGR4 and LGR5 are R-spondin receptors mediating Wnt/β-catenin and Wnt/PCP signalling
- PMID: 21909076
- PMCID: PMC3185347
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2011.175
LGR4 and LGR5 are R-spondin receptors mediating Wnt/β-catenin and Wnt/PCP signalling
Abstract
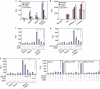
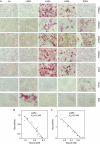
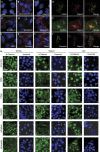
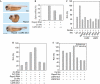
R-spondins are secreted Wnt signalling agonists, which regulate embryonic patterning and stem cell proliferation, but whose mechanism of action is poorly understood. Here we show that R-spondins bind to the orphan G-protein-coupled receptors LGR4 and LGR5 by their Furin domains. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments in mammalian cells and Xenopus embryos indicate that LGR4 and LGR5 promote R-spondin-mediated Wnt/β-catenin and Wnt/PCP signalling. R-spondin-triggered β-catenin signalling requires Clathrin, while Wnt3a-mediated β-catenin signalling requires Caveolin-mediated endocytosis, suggesting that internalization has a mechanistic role in R-spondin signalling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aoki M, Mieda M, Ikeda T, Hamada Y, Nakamura H, Okamoto H (2006) R-spondin3 is required for mouse placental development. Dev Biol 301: 218–226 - PubMed
-
- Barker N, Clevers H (2010) Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptors as markers of adult stem cells. Gastroenterology 138: 1681–1696 - PubMed
-
- Blaydon DC et al. (2006) The gene encoding R-spondin 4 (RSPO4), a secreted protein implicated in Wnt signaling, is mutated in inherited anonychia. Nat Genet 38: 1245–1247 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

