Genome-wide association study identifies six new loci influencing pulse pressure and mean arterial pressure
- PMID: 21909110
- PMCID: PMC3445021
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.922
Genome-wide association study identifies six new loci influencing pulse pressure and mean arterial pressure
Abstract
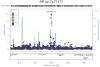
Numerous genetic loci have been associated with systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) in Europeans. We now report genome-wide association studies of pulse pressure (PP) and mean arterial pressure (MAP). In discovery (N = 74,064) and follow-up studies (N = 48,607), we identified at genome-wide significance (P = 2.7 × 10(-8) to P = 2.3 × 10(-13)) four new PP loci (at 4q12 near CHIC2, 7q22.3 near PIK3CG, 8q24.12 in NOV and 11q24.3 near ADAMTS8), two new MAP loci (3p21.31 in MAP4 and 10q25.3 near ADRB1) and one locus associated with both of these traits (2q24.3 near FIGN) that has also recently been associated with SBP in east Asians. For three of the new PP loci, the estimated effect for SBP was opposite of that for DBP, in contrast to the majority of common SBP- and DBP-associated variants, which show concordant effects on both traits. These findings suggest new genetic pathways underlying blood pressure variation, some of which may differentially influence SBP and DBP.
Conflict of interest statement
A.C. is managed by Johns Hopkins Medicine. I.B. and spouse own stock in Incyte Ltd and GlaxoSmithKline. A.N.P is an employee of Amgen. G.F.M. is owner of Cardiovascular Engineering, Inc, a company that designs and manufactures devices that measure vascular stiffness. The company uses these devices in clinical studies that evaluate the effects of diseases and interventions on vascular stiffness. V.M. is an employee of GlaxoSmithKline plc. A.Plump is an employee of Merck and Co, Inc.
Figures








References
-
- Lawes CM, et al. Blood pressure and the global burden of disease 2000. Part II: estimates of attributable burden. J Hypertens. 2006;24:423–30. - PubMed
-
- Rose G. Strategies of prevention: the individual and the population. In: Marmot M, E P, editors. Coronary heart disease epidemiology: From aetiology to Public health. Oxford University Press; Oxford: 2005. pp. 631–41.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- G0801056/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01 HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G1000143/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127592696/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0701863/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC055015/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0902313/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0700704/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC085079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106188470/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K23 HL080025/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ETM/55/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/505/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/710/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- G9521010/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0700931/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U137686857/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601966/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01 AG012109/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F019394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U127592696/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U10 HL054512/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

