Hydrocarbon productivities in different Botryococcus strains: comparative methods in product quantification
- PMID: 21909190
- PMCID: PMC3143338
- DOI: 10.1007/s10811-010-9577-8
Hydrocarbon productivities in different Botryococcus strains: comparative methods in product quantification
Abstract
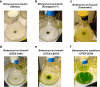
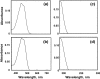
Six different strains of the green microalgae Botryococcus belonging to the A-race or B-race, accumulating alkadiene or botryococcene hydrocarbons, respectively, were compared for biomass and hydrocarbon productivities. Biomass productivity was assessed gravimetrically upon strain growth in the laboratory under defined conditions. Hydrocarbon productivities were measured by three different and independent experimental approaches, including density equilibrium of the intact cells and micro-colonies, spectrophotometric analysis of hydrocarbon extracts, and gravimetric quantitation of eluted hydrocarbons. All three hydrocarbon-quantitation methods yielded similar results for each of the strains examined. The B-race microalgae Botryococcus braunii var. Showa and Kawaguchi-1 constitutively accumulated botryococcene hydrocarbons equivalent to 30% and 20%, respectively, of their overall biomass. The A-race microalgae Botryococcus braunii, varieties Yamanaka, UTEX 2441 and UTEX LB572 constitutively accumulated alkadiene hydrocarbons ranging from 14% to 13% and 10% of their overall biomass, respectively. Botryococcus sudeticus (UTEX 2629), a morphologically different green microalga, had the lowest hydrocarbon accumulation, equal to about 3% of its overall biomass. Results validate the density equilibrium and spectrophotometric analysis methods in the quantitation of botryococcene-type hydrocarbons. These analytical advances will serve in the screening and selection of B. braunii and of other microalgae in efforts to identify those having a high hydrocarbon content for use in commercial applications.
Figures




References
-
- An JY, Sim SJ, Lee JS, Kim BW. Hydrocarbon production from secondarily treated piggery wastewater by the green alga Botryococcus braunii. J Appl Phycol. 2003;15(2/3):185–191. doi: 10.1023/A:1023855710410. - DOI
-
- Bachofen R. The production of hydrocarbons by Botryococcus braunii. Experientia. 1982;38:47–49. doi: 10.1007/BF01944526. - DOI
-
- Bailliez C, Largeau C, Casadevall E, Yang LW, Berkaloff C. Photosynthesis, growth and hydrocarbon production of Botryococcus braunii immobilized by entrapment and adsorption in polyurethane foams. Appl Microbiol Biot. 1988;29:141–147.
-
- Beakes GW, Cleary AL. Visualization of plastids and lipophilic components in living colonies of a wild strain of the hydrocarbon-forming, green alga Botryococcus by laser scanning confocal microscopy. J Appl Phycol. 1999;10:435–446. doi: 10.1023/A:1008055613827. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
