A systems biology approach identifies molecular networks defining skeletal muscle abnormalities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 21909251
- PMCID: PMC3164707
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002129
A systems biology approach identifies molecular networks defining skeletal muscle abnormalities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is an inflammatory process of the lung inducing persistent airflow limitation. Extensive systemic effects, such as skeletal muscle dysfunction, often characterize these patients and severely limit life expectancy. Despite considerable research efforts, the molecular basis of muscle degeneration in COPD is still a matter of intense debate. In this study, we have applied a network biology approach to model the relationship between muscle molecular and physiological response to training and systemic inflammatory mediators. Our model shows that failure to co-ordinately activate expression of several tissue remodelling and bioenergetics pathways is a specific landmark of COPD diseased muscles. Our findings also suggest that this phenomenon may be linked to an abnormal expression of a number of histone modifiers, which we discovered correlate with oxygen utilization. These observations raised the interesting possibility that cell hypoxia may be a key factor driving skeletal muscle degeneration in COPD patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
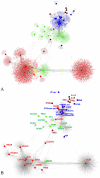
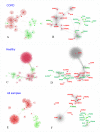

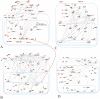
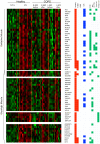

References
-
- Hogg JC, Chu F, Utokaparch S, Woods R, Elliott WM, et al. The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2645–2653. - PubMed
-
- Cosio MG, Saetta M, Agusti A. Immunologic aspects of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2445–2454. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: Global burden of disease study. Lancet. 1997;349:1498–1504. - PubMed
-
- Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. nhlbi/who global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease (gold) workshop summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1256–1276. - PubMed
-
- Rabe KF, Hurd S, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Buist SA, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Gold executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:532–555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

