The regulated secretory pathway in CD4(+) T cells contributes to human immunodeficiency virus type-1 cell-to-cell spread at the virological synapse
- PMID: 21909273
- PMCID: PMC3164651
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002226
The regulated secretory pathway in CD4(+) T cells contributes to human immunodeficiency virus type-1 cell-to-cell spread at the virological synapse
Abstract
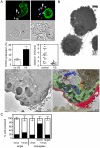
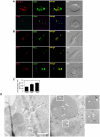
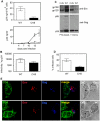
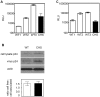
Direct cell-cell spread of Human Immunodeficiency Virus type-1 (HIV-1) at the virological synapse (VS) is an efficient mode of dissemination between CD4(+) T cells but the mechanisms by which HIV-1 proteins are directed towards intercellular contacts is unclear. We have used confocal microscopy and electron tomography coupled with functional virology and cell biology of primary CD4(+) T cells from normal individuals and patients with Chediak-Higashi Syndrome and report that the HIV-1 VS displays a regulated secretion phenotype that shares features with polarized secretion at the T cell immunological synapse (IS). Cell-cell contact at the VS re-orientates the microtubule organizing center (MTOC) and organelles within the HIV-1-infected T cell towards the engaged target T cell, concomitant with polarization of viral proteins. Directed secretion of proteins at the T cell IS requires specialized organelles termed secretory lysosomes (SL) and we show that the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env) localizes with CTLA-4 and FasL in SL-related compartments and at the VS. Finally, CD4(+) T cells that are disabled for regulated secretion are less able to support productive cell-to-cell HIV-1 spread. We propose that HIV-1 hijacks the regulated secretory pathway of CD4(+) T cells to enhance its dissemination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Sattentau Q. Avoiding the void: cell-to-cell spread of human viruses. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6:815–826. - PubMed
-
- Sowinski S, Jolly C, Berninghausen O, Purbhoo MA, Chauveau A, et al. Membrane nanotubes physically connect T cells over long distances presenting a novel route for HIV-1 transmission. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:211–219. - PubMed
-
- Jolly C, Sattentau QJ. Retroviral spread by induction of virological synapses. Traffic. 2004;5:643–650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

