Chalcone synthase and its functions in plant resistance
- PMID: 21909286
- PMCID: PMC3148432
- DOI: 10.1007/s11101-011-9211-7
Chalcone synthase and its functions in plant resistance
Abstract
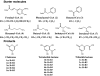
Chalcone synthase (CHS, EC 2.3.1.74) is a key enzyme of the flavonoid/isoflavonoid biosynthesis pathway. Besides being part of the plant developmental program the CHS gene expression is induced in plants under stress conditions such as UV light, bacterial or fungal infection. CHS expression causes accumulation of flavonoid and isoflavonoid phytoalexins and is involved in the salicylic acid defense pathway. This review will discuss CHS and its function in plant resistance.
Figures



References
-
- Amedeo P, Habu Y, Afsar K, Scheid OM, Paszkowski J. Disruption of the plant gene MOM releases transcriptional silencing of methylated genes. Nature. 2000;405:203–206. - PubMed
-
- Bohm BA. Introduction to flavonoids. Amsterdam: Hardwood Academic Publishers; 1998.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
