Cleavage of von Willebrand factor by granzyme M destroys its factor VIII binding capacity
- PMID: 21909423
- PMCID: PMC3164717
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024216
Cleavage of von Willebrand factor by granzyme M destroys its factor VIII binding capacity
Abstract
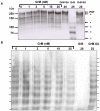
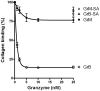
Von Willebrand factor (VWF) is a pro-hemostatic multimeric plasma protein that promotes platelet aggregation and stabilizes coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) in plasma. The metalloproteinase ADAMTS13 regulates the platelet aggregation function of VWF via proteolysis. Severe deficiency of ADAMTS13 is associated with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, but does not always correlate with its clinical course. Therefore, other proteases could also be important in regulating VWF activity. In the present study, we demonstrate that VWF is cleaved by the cytotoxic lymphocyte granule component granzyme M (GrM). GrM cleaved both denaturated and soluble plasma-derived VWF after Leu at position 276 in the D3 domain. GrM is unique in that it did not affect the multimeric size and pro-hemostatic platelet aggregation ability of VWF, but instead destroyed the binding of VWF to FVIII in vitro. In meningococcal sepsis patients, we found increased plasma GrM levels that positively correlated with an increased plasma VWF/FVIII ratio in vivo. We conclude that, next to its intracellular role in triggering apoptosis, GrM also exists extracellularly in plasma where it could play a physiological role in controlling blood coagulation by determining plasma FVIII levels via proteolytic processing of its carrier VWF.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of multimerization of human and recombinant von Willebrand factor on platelet aggregation, binding to collagen and binding of coagulation factor VIII.Thromb Res. 1996 Oct 1;84(1):55-66. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(96)00161-2. Thromb Res. 1996. PMID: 8885147
-
[von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease].Rinsho Ketsueki. 2016;57(10):2113-2123. doi: 10.11406/rinketsu.57.2113. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2016. PMID: 27795521 Japanese.
-
Platelet receptors for human Factor VIII/von Willebrand protein: functional correlation of receptor occupancy and ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5317-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5317. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979. PMID: 315561 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Roles of the von Willebrand Factor-Factor VIII Interaction.Subcell Biochem. 2020;94:437-464. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-41769-7_18. Subcell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32189311 Review.
-
Von Willebrand factor: another janus-faced hemostasis protein.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2008 Oct;34(7):663-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1104545. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2008. PMID: 19085767 Review.
Cited by
-
Granzyme K synergistically potentiates LPS-induced cytokine responses in human monocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Apr 22;111(16):5974-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1317347111. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24711407 Free PMC article.
-
Tripartite factors leading to molecular divergence between human and murine smooth muscle.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 16;15(1):e0227672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227672. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31945134 Free PMC article.
-
Granzymes in health and diseases: the good, the bad and the ugly.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 5;15:1371743. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1371743. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38646541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acquired von Willebrand syndrome associated with left ventricular assist device.Blood. 2016 Jun 23;127(25):3133-41. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-10-636480. Epub 2016 May 3. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27143258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Granzyme M: behind enemy lines.Cell Death Differ. 2014 Mar;21(3):359-68. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.189. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Cell Death Differ. 2014. PMID: 24413154 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ruggeri ZM. Structure and function of von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82:576–584. - PubMed
-
- Ruggeri ZM. Von Willebrand factor, platelets and endothelial cell interactions. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:1335–1342. - PubMed
-
- Levy GG, Nichols WC, Lian EC, Foroud T, McClintick JN, et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature. 2001;413:488–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

