Allopurinol reduces the lethality associated with acute renal failure induced by Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom: comparison with probenecid
- PMID: 21909449
- PMCID: PMC3167791
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001312
Allopurinol reduces the lethality associated with acute renal failure induced by Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom: comparison with probenecid
Abstract
Background: Acute renal failure is one of the most serious complications of envenoming resulting from Crotalus durissus terrificus bites. This study evaluated the relevance of hyperuricemia and oxidative stress and the effects of allopurinol and probenecid in renal dysfunction caused by direct nephrotoxicity of C. d. terrificus venom.
Methodology/principal findings: Hematocrit, protein, renal function and redox status were assessed in mice. High ratio of oxidized/reduced glutathione and hyperuricemia induced by C. d. terrificus venom were ameliorated by both, allopurinol or probenecid, but only allopurinol significantly reduced the lethality caused by C. d. terrificus venom. The effectiveness of probenecid is compromised probably because it promoted hypercreatinemia and hypocreatinuria and worsed the urinary hypo-osmolality in envenomed mice. In turn, the highest effectiveness of allopurinol might be due to its ability to diminish the intracellular formation of uric acid.
Conclusions/significance: Data provide consistent evidences linking uric acid with the acute renal failure induced by C. d. terrificus venom, as well as that this envenoming in mice constitutes an attractive animal model suitable for studying the hyperuricemia and that the allopurinol deserves to be clinically evaluated as an approach complementary to anti-snake venom serotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
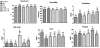




References
-
- Brazilian Ministry of Health. Manual de Diagnostico e Tratamento de Acidentes por Animais Peconhentos. 2nd edition. Brasília, Brazil: Fundacao Nacional de Saude; 2001.
-
- Luzia S, Cruz LS, Vargas R, Lopes AA. Snakebite envenomation and death in the developing world. Ethnicity & Disease. 2009;19[Suppl1]:S142–S146. - PubMed
-
- Sitprija V. Snakebite nephropathy. Nephrology. 2006;11:442–448. - PubMed
-
- Pinho FM, Zanneta DM, Burdmann EA. Acute renal failure after Crotalus durissus snakebite: a prospective survey on 100 patients. Kidney Int. 2005;67:659–667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

