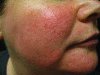
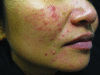
A Guide to the Ingredients and Potential Benefits of Over-the-Counter Cleansers and Moisturizers for Rosacea Patients
- PMID: 21909456
- PMCID: PMC3168246
A Guide to the Ingredients and Potential Benefits of Over-the-Counter Cleansers and Moisturizers for Rosacea Patients
Abstract
It is difficult for rosacea patients to discern which products and ingredients will be beneficial to their skin and which products will lead to an exacerbation of the signs and symptoms of rosacea. In this paper, the authors provide a brief overview of rosacea, its pathogenesis, signs and symptoms, and the management of the two major rosacea subtypes-erythematotelangiectatic rosacea and papular pustular rosacea. Reviewed in greater detail are the common ingredients used in over-the-counter cleansers and moisturizers with discussion of how these ingredients potentially benefit or harm the skin of patients with rosacea. Clinical studies investigating the benefits of using certain over-the-counter cleansers and moisturizers in patients with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea and papular pustular rosacea with or without topical prescription therapy are also reviewed. The specific formulas used in the clinical studies include a sensitive skin synthetic detergent bar, a nonalkaline cleanser and moisturizer, polyhydroxy acid containing cleanser and moisturizer, and a ceramide-based cleanser and moisturizer formulated in a multivesicular emulsion. Based on review of available data, the authors conclude that the use of mild over-the-counter cleansers and moisturizers is beneficial for patients with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea and papular pustular rosacea. The properties of over-the-counter cleansers and moisturizers that contribute to their mildness include an acidic-neutral pH to minimize the flux in skin pH; surfactants or emulsifiers that will not strip the skin of its moisture or strip the lipids and proteins of the stratum corneum; moisturizing ingredients such as emollients, humectants, and occlusives; and formulas without potential irritants and allergens. The most consistent clinical benefits demonstrated in the reviewed studies were a subjectively perceived improvement in subjective symptoms of dryness and irritation as well as an objective improvement in dryness.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Moisturizer in Patients with Inflammatory Skin Diseases.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jul 1;58(7):888. doi: 10.3390/medicina58070888. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35888607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Choosing the Right Partner: Complementing Prescription Acne Medication With Over-the-Counter Cleansers and Moisturizers.J Drugs Dermatol. 2020 Nov 1;19(11):1069-1075. doi: 10.36849/JDD.2020.5536. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 33196748 Review.
-
Cleansing without compromise: the impact of cleansers on the skin barrier and the technology of mild cleansing.Dermatol Ther. 2004;17 Suppl 1:16-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1396-0296.2004.04s1002.x. Dermatol Ther. 2004. PMID: 14728695 Review.
-
Role of topical emollients and moisturizers in the treatment of dry skin barrier disorders.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4(11):771-88. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200304110-00005. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 14572299 Review.
-
Niacinamide-containing facial moisturizer improves skin barrier and benefits subjects with rosacea.Cutis. 2005 Aug;76(2):135-41. Cutis. 2005. PMID: 16209160 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Lactonic Sophorolipids Increase Tumor Burden in Apcmin+/- Mice.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 6;11(6):e0156845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156845. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27271048 Free PMC article.
-
Moisturizer in Patients with Inflammatory Skin Diseases.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jul 1;58(7):888. doi: 10.3390/medicina58070888. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35888607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin hydration is significantly increased by a cream formulated to mimic the skin's own natural moisturizing systems.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018 Oct 15;11:491-497. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S177697. eCollection 2018. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 30410378 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Assessing Burning and Stinging when Managing Rosacea: A Review.Acta Derm Venereol. 2021 Oct 31;101(10):adv00584. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v101.356. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021. PMID: 34643244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinical relevance of maintaining the functional integrity of the stratum corneum in both healthy and disease-affected skin.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011 Sep;4(9):22-42. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21938268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Loden M. Role of topical emollients and moisturizers in the treatment of dry skin barrier disorders. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4(11):771–778. - PubMed
-
- Crawford GH, Pelle MH, and James WD. Rosacea: I. Etiology, pathogenesis, and subtype classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004:327–341. - PubMed
-
- Del Rosso JQ. The use of moisturizers as an integral component of topical therapy for rosacea: clinical results based on assessment of skin characteristic study. Cutis. 2009;84:72–76. - PubMed
-
- Lonne-Rahm SB, Fischer T, Berg M. Stinging and rosacea. Acta Derm Venerol. 1999;79:460–461. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources