Changes in nonstructural protein 3 are associated with attenuation in avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus
- PMID: 21909766
- PMCID: PMC7089577
- DOI: 10.1007/s11262-011-0668-7
Changes in nonstructural protein 3 are associated with attenuation in avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus
Abstract
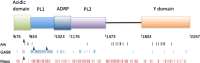
Full-length genome sequencing of pathogenic and attenuated (for chickens) avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) strains of the same serotype was conducted to identify genetic differences between the pathotypes. Analysis of the consensus full-length genome for three different IBV serotypes (Ark, GA98, and Mass41) showed that passage in embryonated eggs, to attenuate the viruses for chickens, resulted in 34.75-43.66% of all the amino acid changes occurring in nsp 3 within a virus type, whereas changes in the spike glycoprotein, thought to be the most variable protein in IBV, ranged from 5.8 to 13.4% of all changes. The attenuated viruses did not cause any clinical signs of disease and had lower replication rates than the pathogenic viruses of the same serotype in chickens. However, both attenuated and pathogenic viruses of the same serotype replicated similarly in embryonated eggs, suggesting that mutations in nsp 3, which is involved in replication of the virus, might play an important role in the reduced replication observed in chickens leading to the attenuated phenotype.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of Amino Acids within Nonstructural Proteins 10 and 14 of the Avian Coronavirus Infectious Bronchitis Virus That Result in Attenuation In Vivo and In Ovo.J Virol. 2022 Mar 23;96(6):e0205921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02059-21. Epub 2022 Jan 19. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35044208 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant infectious bronchitis virus containing mutations in non-structural proteins 10, 14, 15, and 16 and within the macrodomain provides complete protection against homologous challenge.J Virol. 2025 Apr 15;99(4):e0166324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01663-24. Epub 2025 Feb 27. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40013770 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity of avian infectious bronchitis coronavirus in recent years in China.Avian Dis. 2012 Mar;56(1):15-28. doi: 10.1637/9804-052011-Reg.1. Avian Dis. 2012. PMID: 22545524
-
Avian infectious bronchitis virus.Rev Sci Tech. 2000 Aug;19(2):493-508. doi: 10.20506/rst.19.2.1228. Rev Sci Tech. 2000. PMID: 10935276 Review.
-
Review of infectious bronchitis virus around the world.Avian Dis. 2012 Dec;56(4):634-41. doi: 10.1637/10227-043012-Review.1. Avian Dis. 2012. PMID: 23397833 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Characterization of the Belgian Nephropathogenic Infectious Bronchitis Virus (NIBV) Reference Strain B1648.Viruses. 2015 Aug 7;7(8):4488-506. doi: 10.3390/v7082827. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26262637 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of Infectious Bronchitis Virus in Eggs Results in Different Patterns of Genomic Variation across Multiple Replicates.J Virol. 2019 Jun 28;93(14):e00492-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00492-19. Print 2019 Jul 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31043525 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Alterations of the Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV) Strain of the GI-23 Lineage Induced by Passages in Chickens and Quails.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 28;26(9):4200. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094200. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362437 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the complete genomic sequences of two virus subpopulations of the Australian infectious bronchitis virus vaccine VicS.Avian Pathol. 2015;44(3):182-91. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2015.1022857. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Avian Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25721384 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic sequence changes related to the attenuation of avian infectious bronchitis virus strain TW2575/98.Virus Genes. 2020 Jun;56(3):369-379. doi: 10.1007/s11262-020-01753-5. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Virus Genes. 2020. PMID: 32232712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cavanagh D, Gelb J., Jr . Infectioius bronchitis. In: Saif YM, Fadley AM, Glisson JR, McDougald LR, Nolan LK, Swayne DE, editors. Diseases of poultry. Ames: Blackwell Publishing; 2008. pp. 117–135.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

