Challenges in echocardiographic assessment of mitral regurgitation in children after repair of atrioventricular septal defect
- PMID: 21909774
- PMCID: PMC3265615
- DOI: 10.1007/s00246-011-0107-5
Challenges in echocardiographic assessment of mitral regurgitation in children after repair of atrioventricular septal defect
Abstract
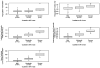
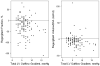
The validity and reproducibility of echocardiographic methods used to quantify mitral regurgitation (MR) in children with congenital heart disease are unknown. We evaluated the usefulness of methods used to quantify MR in children enrolled in a multicenter trial of enalapril 6 months after surgical repair of an atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD). MR severity in this trial was assessed using body surface area (BSA)-adjusted vena contracta lateral (i-VCW(lat)) and anterior-posterior (i-VCW(ap)) dimensions and cross-sectional area (i-VCA), regurgitant volume/BSA, regurgitant fraction, and qualitative MR grade. For each method, association with left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDVz) and end-diastolic dimension (LVEDDz) z-scores and interobserver agreement were assessed. In 149 children (median age 1 year), i-VCW(lat), i-VCW(ap), and i-VCA were best associated with LVEDVz (r (2) = 0.54, r (2) = 0.24, and r (2) = 0.46, respectively; p < 0.001 for all) and showed the highest interobserver agreement (intraclass correlation coefficient = 0.62, 0.73, and 0.68, respectively). Qualitative MR grade was also associated with LVEDVz (r (2) = 0.31, p < 0.001) and showed modest interobserver agreement (kappa 0.56). Regurgitant volume/BSA and regurgitant fraction were associated with LVEDVz (r (2) = 0.45 and r (2) = 0.45, p < 0.001 for both) but showed poor interobserver agreement [ICC = 0.28 (n = 91) and ICC = 0.17 (n = 76), respectively], and their values were negative in 75% of subjects. In conclusion, echocardiographic assessment of MR severity after AVSD remains challenging. Among the quantitative methods used in this trial, i-VCW and i-VCA performed the best but offered little advantage compared with qualitative MR grade. The utility of regurgitant volume and fraction was severely limited by poor interobserver agreement and frequently negative values.
Figures

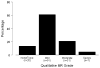



References
-
- Acker MA, Bolling S, Shemin R, Kirklin J, Oh JK, Mann DL, Jessup M, Sabbah HN, Starling RC, Kubo SH. Mitral valve surgery in heart failure: Insights from the Acorn Clinical Trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;132:568–577. - PubMed
-
- Biner S, Rafique A, Rafii F, Tolstrup K, Noorani O, Shiota T, Gurudevan S, Siegel RJ. Reproducibility of proximal isovelocity surface area, vena contracta, and regurgitant jet area for assessment of mitral regurgitation severity. J Am Coll Cardiol Imag. 2010;3:235–243. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2009.09.029. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury UK, Airan B, Malhotra A, Bisoi AK, Kalaivani M, Govindappa RM, Venugopal P. Specific issues after surgical repair of partial atrioventricular septal defect: actuarial survival, freedom from reoperation, fate of the left atrioventricular valve, prevalence of left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, and other events. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;137:548–555. e542. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2008.04.035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dujardin KS, Enriquez-Sarano M, Bailey KR, Nishimura RA, Seward JB, Tajik AJ. Grading of mitral regurgitation by quantitative Doppler echocardiography: calibration by left ventricular angiography in routine clinical practice. Circulation. 1997;96:3409–3415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HL068288/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068285/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068279/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068269/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068279/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068288/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068269/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068285/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

