In vitro and in vivo reactivity to fungal cell wall agents in sarcoidosis
- PMID: 21910725
- PMCID: PMC3193923
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04456.x
In vitro and in vivo reactivity to fungal cell wall agents in sarcoidosis
Abstract
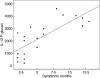
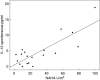
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease. Epidemiological and treatment studies suggest that fungi play a part in the pathogenesis. The aim of this work was to study the effect of fungal cell wall agents (FCWA) on the in vitro secretion of cytokines from peripheral blood monocytes from subjects with sarcoidosis and relate the results to fungal exposure at home and clinical findings. Subjects with sarcoidosis (n=22) and controls (n=20) participated. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stimulated with soluble or particulate β-glucan (S-glucan, P-glucan), chitin or lipopolysaccharide (LPS), whereafter tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10 and IL-12 were measured. The severity of sarcoidosis was determined using a chest X-ray-based score. Serum cytokines (IL-2R, IL-6, IL-10 and IL-12) were determined. To measure domestic fungal exposure, air in the bedrooms was sampled on filters. N-acetylhexosaminidase (NAHA) on the filters was measured as a marker of fungal cell biomass. The induced secretion of cytokines was higher from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from subjects with sarcoidosis. P-glucan was more potent than S-glucan inducing a secretion. Chitin had a small effect. Among subjects with sarcoidosis there was a significant relation between the spontaneous PBMC production of IL-6, IL-10 and IL-12 and the NAHA levels at home. The P-glucan induced secretion of IL-12 was related to the duration of symptoms at the time of diagnosis. Their X-ray scores were related to an increased secretion of cytokines after stimulation with LPS or P-glucan. Subjects with sarcoidosis have a higher reactivity to FCWA in vitro and to home exposure. The influence of FCWA on inflammatory cells and their interference with the inflammatory defense mechanisms in terms of cytokine secretion could be important factors for the development of sarcoidosis.
© 2011 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Immunology © 2011 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fungal cell wall agents suppress the innate inflammatory cytokine responses of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells challenged with lipopolysaccharide in vitro.Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Aug;11(8):939-47. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.02.006. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21329777
-
Fungal exposure and low levels of IL-10 in patients with sarcoidosis.Pulm Med. 2014;2014:164565. doi: 10.1155/2014/164565. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Pulm Med. 2014. PMID: 25180094 Free PMC article.
-
Effects after inhalation of (1-->3)-beta-D-glucan and relation to mould exposure in the home.Mediators Inflamm. 2002 Jun;11(3):149-53. doi: 10.1080/09622935020138181. Mediators Inflamm. 2002. PMID: 12137243 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exploiting fungal cell wall components in vaccines.Semin Immunopathol. 2015 Mar;37(2):199-207. doi: 10.1007/s00281-014-0460-6. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Semin Immunopathol. 2015. PMID: 25404118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Modulation of cytokine production from human mononuclear cells by several agents].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2000 Dec;120(12):1277-90. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.120.12_1277. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2000. PMID: 11193379 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Trained immunity as a possible newcomer in autoinflammatory and autoimmune diseases pathophysiology.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 10;9:1085339. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1085339. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36743677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Trained Immunity in Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Disorders.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 20;9:298. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00298. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29515591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expression profiles in granuloma tissue reveal novel diagnostic markers in sarcoidosis.Exp Mol Pathol. 2014 Jun;96(3):393-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2014.04.006. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Exp Mol Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24768588 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Occupational, Recreational, and Environmental Associations in Patients With Clinically Manifest Cardiac Sarcoidosis.CJC Open. 2020 Jul 17;2(6):585-591. doi: 10.1016/j.cjco.2020.07.010. eCollection 2020 Nov. CJC Open. 2020. PMID: 33305219 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of serum interleukin-10 level of fungal exposure among patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis and healthy people.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2018;35(4):294-298. doi: 10.36141/svdld.v35i4.6757. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2018. PMID: 32476916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hill TA, Lightman S, Pantelidis P, Abdallah A, Spagnolo P, du Bois RM. Intracellular cytokine profiles and T cell activation in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Cytokine. 2008;42:289–92. - PubMed
-
- Zissel G, Prasse A, Müller-Querheim J. Immunologic response of sarcoidosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31:390–403. - PubMed
-
- Gerke A, Hunnunghake G. The immunology of sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2008;29:379–90. - PubMed
-
- S-i N, Miyazaki E, Ando M, et al. Circulating levels of both Th1 and Th2 chemokines are elevated in patients with sarcoidosis. Respir Med. 2008;102:239–47. - PubMed
-
- Mroz RM, Korniluk M, Stasiak-Barmuta A, Chyczewska E. Increased levels of interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008;59(Suppl 6):507–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

