Metabolic engineering of the L-phenylalanine pathway in Escherichia coli for the production of S- or R-mandelic acid
- PMID: 21910908
- PMCID: PMC3182895
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-10-71
Metabolic engineering of the L-phenylalanine pathway in Escherichia coli for the production of S- or R-mandelic acid
Abstract
Background: Mandelic acid (MA), an important component in pharmaceutical syntheses, is currently produced exclusively via petrochemical processes. Growing concerns over the environment and fossil energy costs have inspired a quest to develop alternative routes to MA using renewable resources. Herein we report the first direct route to optically pure MA from glucose via genetic modification of the L-phenylalanine pathway in E. coli.
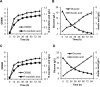
Results: The introduction of hydroxymandelate synthase (HmaS) from Amycolatopsis orientalis into E. coli led to a yield of 0.092 g/L S-MA. By combined deletion of competing pathways, further optimization of S-MA production was achieved, and the yield reached 0.74 g/L within 24 h. To produce R-MA, hydroxymandelate oxidase (Hmo) from Streptomyces coelicolor and D-mandelate dehydrogenase (DMD) from Rhodotorula graminis were co-expressed in an S-MA-producing strain, and the resulting strain was capable of producing 0.68 g/L R-MA. Finally, phenylpyruvate feeding experiments suggest that HmaS is a potential bottleneck to further improvement in yields.
Conclusions: We have constructed E. coli strains that successfully accomplished the production of S- and R-MA directly from glucose. Our work provides the first example of the completely fermentative production of S- and R-MA from renewable feedstock.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Metabolic engineering of the E. coli L-phenylalanine pathway for the production of D-phenylglycine (D-Phg).Metab Eng. 2006 May;8(3):196-208. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2005.12.001. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Metab Eng. 2006. PMID: 16466681
-
Engineering of hydroxymandelate synthases and the aromatic amino acid pathway enables de novo biosynthesis of mandelic and 4-hydroxymandelic acid with Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Metab Eng. 2018 Jan;45:246-254. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Metab Eng. 2018. PMID: 29330068
-
Heterologous pathway for the production of L-phenylglycine from glucose by E. coli.J Biotechnol. 2014 Sep 30;186:91-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.06.033. Epub 2014 Jul 8. J Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25011099
-
Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli for production of L-phenylalanine-derived compounds.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Apr 15;37(5):84. doi: 10.1007/s11274-021-03050-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33855641 Review.
-
Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of phenylpyruvate derivatives.Metab Eng. 2015 Nov;32:55-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2015.09.007. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Metab Eng. 2015. PMID: 26386181 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering Escherichia coli for production of 4-hydroxymandelic acid using glucose-xylose mixture.Microb Cell Fact. 2016 May 27;15:90. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0489-4. Microb Cell Fact. 2016. PMID: 27234226 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic applications of metabolomics in metabolic engineering.Metabolites. 2012 Dec 14;2(4):1090-122. doi: 10.3390/metabo2041090. Metabolites. 2012. PMID: 24957776 Free PMC article.
-
Production of (R)-mandelic acid from styrene, L-phenylalanine, glycerol, or glucose via cascade biotransformations.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2021 Mar 4;8(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40643-021-00374-6. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2021. PMID: 38650227 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering Escherichia coli to overproduce aromatic amino acids and derived compounds.Microb Cell Fact. 2014 Sep 9;13(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12934-014-0126-z. Microb Cell Fact. 2014. PMID: 25200799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Engineering of the Shikimate Pathway for Production of Aromatics and Derived Compounds-Present and Future Strain Construction Strategies.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018 Mar 26;6:32. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00032. eCollection 2018. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29632862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Furlemmeier A, Quitt P, Vogler K, Lanz P. 6-Acyl derivatives of aminopenicillanic acid. US Patent. 1976;3:957–758.
-
- Chang TL, Teleshova N, Rapista A, Paluch M, Anderson RA, Waller DP, Zaneveld LJD, Granelli-Piperno A, Klotman ME. SAMMA, a mandelic acid condensation polymer, inhibits dendritic cell-mediated HIV transmission. FEBS Lett. 2007;581(24):4596–4602. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.08.048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saravanan P, Singh VK. An efficient synthesis of chiral nonracemic diamines: application in asymmetric synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998;39:167–170. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(97)10578-0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

