Are diagnostic criteria for acute malnutrition affected by hydration status in hospitalized children? A repeated measures study
- PMID: 21910909
- PMCID: PMC3180351
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2891-10-92
Are diagnostic criteria for acute malnutrition affected by hydration status in hospitalized children? A repeated measures study
Abstract
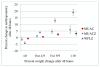
Introduction: Dehydration and malnutrition commonly occur together among ill children in developing countries. Dehydration (change in total body water) is known to alter weight. Although muscle tissue has high water content, it is not known whether mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC) may be altered by changes in tissue hydration. We aimed to determine whether rehydration alters MUAC, MUAC Z score (MUACz), weight-for-length Z-score (WFLz) and classification of nutritional status among hospitalised Kenyan children admitted with signs of dehydration. STUDY PROCEDURE: We enrolled children aged from 3 months to 5 years admitted to a rural Kenyan district hospital with clinical signs compatible with dehydration, and without kwashiorkor. Anthropometric measurements were taken at admission and repeated after 48 hours of treatment, which included rehydration by WHO protocols. Changes in weight observed during this period were considered to be due to changes in hydration status.
Results: Among 325 children (median age 11 months) the median weight gain (rehydration) after 48 hours was 0.21 kg, (an increase of 2.9% of admission body weight). Each 1% change in weight was associated with a 0.40 mm (95% CI: 0.30 to 0.44 mm, p < 0.001) change in MUAC, 0.035z (95% CI: 0.027 to 0.043z, P < 0.001) change in MUACz score and 0.115z (95% CI: 0.114 to 0.116 z, p < 0.001) change in WFLz. Among children aged 6 months or more with signs of dehydration at admission who were classified as having severe acute malnutrition (SAM) at admission by WFLz <-3 or MUAC <115 mm, 21% and 19% of children respectively were above these cut offs after 48 hours.
Conclusion: MUAC is less affected by dehydration than WFLz and is therefore more suitable for nutritional assessment of ill children. However, both WFLz and MUAC misclassify SAM among dehydrated children. Nutritional status should be re-evaluated following rehydration, and management adjusted accordingly.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arm circumference for age, arm circumference and weight-for-height z-score for the evaluation of severe acute malnutrition: a retrospective cohort study in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo.BMC Public Health. 2024 Feb 23;24(1):587. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18083-y. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38395784 Free PMC article.
-
Midupper Arm Circumference Outperforms Weight-Based Measures of Nutritional Status in Children with Diarrhea.J Nutr. 2015 Jul;145(7):1582-7. doi: 10.3945/jn.114.209718. Epub 2015 May 13. J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25972523 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of severe malnutrition among hospitalized children in rural Kenya: comparison of weight for height and mid upper arm circumference.JAMA. 2005 Aug 3;294(5):591-7. doi: 10.1001/jama.294.5.591. JAMA. 2005. PMID: 16077053
-
Severely malnourished children with a low weight-for-height have similar mortality to those with a low mid-upper-arm-circumference: II. Systematic literature review and meta-analysis.Nutr J. 2018 Sep 15;17(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12937-018-0383-5. Nutr J. 2018. PMID: 30217196 Free PMC article.
-
Family-led mid-upper arm circumference (FL-MUAC) approach and the screening of acute malnutrition in children aged 6 to 59 months in Africa: a scoping review.Pan Afr Med J. 2024 Oct 11;49:38. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2024.49.38.36956. eCollection 2024. Pan Afr Med J. 2024. PMID: 39886109 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mid-upper arm circumference v. weight-for-height Z-score for predicting mortality in hospitalized children under 5 years of age.Public Health Nutr. 2016 Oct;19(14):2513-20. doi: 10.1017/S1368980016000719. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Public Health Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27049813 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a Smartphone Decision-Support Tool for Diarrheal Disease Management in a Resource-Limited Setting.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Jan 19;11(1):e0005290. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005290. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28103233 Free PMC article.
-
Severe acute malnutrition and infection.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2014 Dec;34 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S1-S29. doi: 10.1179/2046904714Z.000000000218. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2014. PMID: 25475887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and assemblage of Giardia duodenalis in a case-control study of children under 5 years from Jimma, Southwest Ethiopia.Parasitol Res. 2023 Dec 13;123(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s00436-023-08029-5. Parasitol Res. 2023. PMID: 38091122 Free PMC article.
-
Do we need to reconsider the CMAM admission and discharge criteria?; an analysis of CMAM data in South Sudan.BMC Public Health. 2020 Apr 16;20(1):511. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-08657-x. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32299403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The WHO Child Growth Standards. http://www.who.int/childgrowth/standards/en/
-
- Myatt M, Khara T, Collins S. A review of methods to detect cases of severely malnourished children in the community for their admission into community-based therapeutic care programs. Food Nutr Bull. 2006;27(3 Suppl):S7–23. - PubMed
-
- Brambilla P, Rolland-Cachera MF, Testolin C, Briend A, Salvatoni A, Testolin G, Chiumello G. Lean mass of children in various nutritional states. Comparison between dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and anthropometry. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;904:433–436. - PubMed
-
- The arm circumference as a public health index of protein-calorie malnutrition of early childhood. J Trop Pediatr. 1969;15(4):177–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical