Targeted translational regulation using the PUF protein family scaffold
- PMID: 21911377
- PMCID: PMC3179070
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1105151108
Targeted translational regulation using the PUF protein family scaffold
Abstract
Regulatory complexes formed on mRNAs control translation, stability, and localization. These complexes possess two activities: one that binds RNA and another--the effector--that elicits a biological function. The Pumilio and FBF (PUF) protein family of RNA binding proteins provides a versatile scaffold to design and select proteins with new specificities. Here, the PUF scaffold is used to target translational activation and repression of specific mRNAs, and to induce specific poly(A) addition and removal. To do so, we linked PUF scaffold proteins to a translational activator, GLD2, or a translational repressor, CAF1. The chimeric proteins activate or repress the targeted mRNAs in Xenopus oocytes, and elicit poly(A) addition or removal. The magnitude of translational control relates directly to the affinity of the RNA-protein complex over a 100-fold range of K(d). The chimeric proteins act on both reporter and endogenous mRNAs: an mRNA that normally is deadenylated during oocyte maturation instead receives poly(A) in the presence of an appropriate chimera. The PUF-effector strategy enables the design of proteins that affect translation and stability of specific mRNAs in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



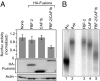
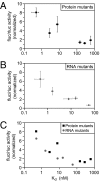


References
-
- Chen CY, Shyu AB. AU-rich elements: Characterization and importance in mRNA degradation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:465–470. - PubMed
-
- Condeelis J, Singer RH. How and why does beta-actin mRNA target? Biol Cell. 2005;97(1):97–110. - PubMed
-
- Crittenden SL, et al. A conserved RNA-binding protein controls germline stem cells in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2002;417:660–663. - PubMed
-
- Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:351–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

