Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use among persons with chronic kidney disease in the United States
- PMID: 21911761
- PMCID: PMC3185478
- DOI: 10.1370/afm.1302
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use among persons with chronic kidney disease in the United States
Abstract
Purpose: Because avoidance of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is recommended for most individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we sought to characterize patterns of NSAID use among persons with CKD in the United States.
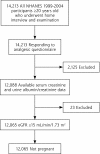
Methods: A total of 12,065 adult (aged 20 years or older) participants in the cross-sectional National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1999-2004) responded to a questionnaire regarding their use of over-the-counter and prescription NSAIDs. NSAIDs (excluding aspirin and acetaminophen) were defined by self-report. CKD was categorized as no CKD, mild CKD (stages 1 and 2; urinary albumin-creatinine ratio of ≥ 30 mg/g) and moderate to severe CKD (stages 3 and 4; estimated glomerular filtration rate of 15-59 mL/min/1.73 m(2)). Adjusted prevalence was calculated using multivariable logistic regression with appropriate population-based weighting.
Results: Current use (nearly every day for 30 days or longer) of any NSAID was reported by 2.5%, 2.5%, and 5.0% of the US population with no, mild, and moderate to severe CKD, respectively; nearly all of the NSAIDs used were available over-the-counter. Among those with moderate to severe CKD who were currently using NSAIDs, 10.2% had a current NSAID prescription and 66.1% had used NSAIDs for 1 year or longer. Among those with CKD, disease awareness was not associated with reduced current NSAID use: (3.8% vs 3.9%, aware vs unaware; P=.979).
Conclusions: Physicians and other health care clinicians should be aware of use of NSAIDs among those with CKD in the United States and evaluate NSAID use in their CKD patients.
Figures



References
-
- Paulose-Ram R, Hirsch R, Dillon C, Losonczy K, Cooper M, Ostchega Y. Prescription and non-prescription analgesic use among the US adult population: results from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2003;12(4):315–326 - PubMed
-
- Goroll AH, Mulley AG, Jr, eds. Primary Care Medicine: Office Evaluation and Management of the Adult Patient. 6th ed Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009
-
- Barker LR, Zieve PD, eds. Principles of Ambulatory Medicine. 7th ed Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007
-
- Fauci AS, ed. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 17th ed New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2008
-
- National Kidney Foundation Kidney disease outcomes quality initiative (K/DOQI). http://www.kidney.org/professionals/doqi
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
