Cure of alopecia areata after eradication of Helicobacter pylori: a new association?
- PMID: 21912461
- PMCID: PMC3158418
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i26.3165
Cure of alopecia areata after eradication of Helicobacter pylori: a new association?
Abstract
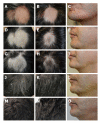
Alopecia areata is a disease of the hair follicles, with strong evidence supporting autoimmune etiology. Alopecia areata is frequently associated with immune-mediated diseases with skin manifestations such as psoriasis and lichen planus, or without skin manifestations such as autoimmune thyroiditis and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is present in around 50% of the world's population and has been associated with a variety of immune-mediated extra-digestive disorders including autoimmune thyroiditis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, and psoriasis. A case of a 43-year old man with an 8-mo history of alopecia areata of the scalp and beard is presented. The patient was being treated by a dermatologist and had psychiatric support, without any improvement. He had a history of dyspepsia and the urea breath test confirmed H. pylori infection. The patient went into remission from alopecia areata after H. pylori eradication. If such an association is confirmed by epidemiological studies designed for this purpose, new therapeutic options could be available for these patients, especially in areas where infection with H. pylori is highly prevalent.
Keywords: Alopecia areata; Eradication treatment; Helicobacter pylori; Molecular mimicry.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenstein ED, Warshauer BL. Alopecia areata and autoimmunity. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:1065. - PubMed
-
- Tan E, Tay YK, Goh CL, Chin Giam Y. The pattern and profile of alopecia areata in Singapore-a study of 219 Asians. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:748–753. - PubMed
-
- Treem WR, Veligati LN, Rotter JI, Targan SR, Hyams JS. Ulcerative colitis and total alopecia in a mother and her son. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:1187–1191. - PubMed
-
- Goh C, Finkel M, Christos PJ, Sinha AA. Profile of 513 patients with alopecia areata: associations of disease subtypes with atopy, autoimmune disease and positive family history. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:1055–1060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

