Crystal structure of C-terminal truncated apolipoprotein A-I reveals the assembly of high density lipoprotein (HDL) by dimerization
- PMID: 21914797
- PMCID: PMC3207425
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.260422
Crystal structure of C-terminal truncated apolipoprotein A-I reveals the assembly of high density lipoprotein (HDL) by dimerization
Abstract
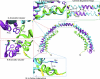
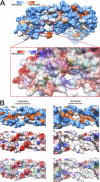
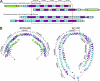
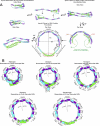
Apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) plays important structural and functional roles in plasma high density lipoprotein (HDL) that is responsible for reverse cholesterol transport. However, a molecular understanding of HDL assembly and function remains enigmatic. The 2.2-Å crystal structure of Δ(185-243)apoA-I reported here shows that it forms a half-circle dimer. The backbone of the dimer consists of two elongated antiparallel proline-kinked helices (five AB tandem repeats). The N-terminal domain of each molecule forms a four-helix bundle with the helical C-terminal region of the symmetry-related partner. The central region forms a flexible domain with two antiparallel helices connecting the bundles at each end. The two-domain dimer structure based on helical repeats suggests the role of apoA-I in the formation of discoidal HDL particles. Furthermore, the structure suggests the possible interaction with lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase and may shed light on the molecular details of the effect of the Milano, Paris, and Fin mutations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lipid-free Apolipoprotein A-I Structure: Insights into HDL Formation and Atherosclerosis Development.Arch Med Res. 2015 Jul;46(5):351-60. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2015.05.012. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Arch Med Res. 2015. PMID: 26048453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein A-I: structure-function relationships.J Lipid Res. 2000 Jun;41(6):853-72. J Lipid Res. 2000. PMID: 10828078 Review.
-
High density lipoprotein particle size restriction in apolipoprotein A-I(Milano) transgenic mice.J Lipid Res. 1997 Nov;38(11):2314-21. J Lipid Res. 1997. PMID: 9392429
-
Effect of the surface lipid composition of reconstituted LPA-I on apolipoprotein A-I structure and lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase activity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Feb 16;1390(2):160-72. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2760(97)00172-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9507105
-
A Systematic Investigation of Structure/Function Requirements for the Apolipoprotein A-I/Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase Interaction Loop of High-density Lipoprotein.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 18;291(12):6386-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.696088. Epub 2016 Jan 21. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26797122 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of apolipoprotein A-II in the structure and remodeling of human high-density lipoprotein (HDL): protein conformational ensemble on HDL.Biochemistry. 2012 Jun 12;51(23):4633-41. doi: 10.1021/bi300555d. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22631438 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insights into Human Hereditary Apolipoprotein A-I Amyloidosis Caused by the Glu34Lys Mutation.Biochemistry. 2018 Oct 2;57(39):5738-5747. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00817. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 30184436 Free PMC article.
-
Microenvironmentally controlled secondary structure motifs of apolipoprotein A-I derived peptides.Mol Cell Biochem. 2014 Aug;393(1-2):99-109. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2050-2. Epub 2014 Apr 20. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24748322 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein-A1 transports and regulates MMP2 in the blood.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 22;16(1):3752. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59062-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40263360 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein A-I helical structure and stability in discoidal high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles by hydrogen exchange and mass spectrometry.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 17;109(29):11687-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209305109. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22745166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heron M., Hoyert D. L., Murphy S. L., Xu J., Kochanek K. D., Tejada-Vera B. (2009) Natl. Vital Stat. Rep. 57, 1–134 - PubMed
-
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. (1995) J. Lipid Res. 36, 211–228 - PubMed
-
- Fielding C. J., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E. (1972) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 46, 1493–1498 - PubMed
-
- Lee J. Y., Parks J. S. (2005) Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 16, 19–25 - PubMed
-
- Acton S., Rigotti A., Landschulz K. T., Xu S., Hobbs H. H., Krieger M. (1996) Science 271, 518–520 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

