Thermodynamic evaluation of ligand binding in the plant-like phosphoethanolamine methyltransferases of the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus
- PMID: 21914812
- PMCID: PMC3207426
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.290619
Thermodynamic evaluation of ligand binding in the plant-like phosphoethanolamine methyltransferases of the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus
Abstract
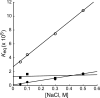
Nematodes are a major cause of disease and the discovery of new pathways not found in hosts is critical for development of therapeutic targets. Previous studies suggest that Caenorhabditis elegans synthesizes phosphocholine via two S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet)-dependent phosphoethanolamine methyltransferases (PMT). Here we examine two PMT from the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus. Sequence analysis suggests that HcPMT1 contains a methyltransferase domain in the N-terminal half of the protein and that HcPMT2 encodes a C-terminal methyltransferase domain, as in the C. elegans proteins. Kinetic analysis demonstrates that HcPMT1 catalyzes the conversion of phosphoethanolamine to phosphomonomethylethanolamine (pMME) and that HcPMT2 methylates pMME to phosphodimethylethanolamine (pDME) and pDME to phosphocholine. The IC(50) values for miltefosine, sinefungin, amodiaquine, diphenhydramine, and tacrine suggest differences in the active sites of these two enzymes. To examine the interaction of AdoMet and S-adenosylhomocysteine (AdoCys), isothermal titration calorimetry confirmed the presence of a single binding site in each enzyme. Binding of AdoMet and AdoCys is tight (K(d) ∼2-25 μm) over a range of temperatures (5-25 °C) and NaCl concentrations (0.05-0.5 m). Heat capacity changes for AdoMet and AdoCys binding suggests that each HcPMT differs in interaction surface area. Nonlinear van't Hoff plots also indicate a possible conformational change upon AdoMet/AdoCys binding. Functional analysis of the PMT from a parasitic nematode provides new insights on inhibitor and AdoMet/AdoCys binding to these enzymes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nematode phospholipid metabolism: an example of closing the genome-structure-function circle.Trends Parasitol. 2014 May;30(5):241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Trends Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24685202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of structure and mechanistic divergence in di-domain methyltransferases from nematode phosphocholine biosynthesis.Structure. 2013 Oct 8;21(10):1778-87. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.07.023. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Structure. 2013. PMID: 24012478 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of phosphoethanolamine transmethylation enzymes decreases viability of Haemonchus contortus.Vet Parasitol. 2016 Jun 15;223:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2016.04.008. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Vet Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27198768
-
In vitro anthelmintic efficacy of inhibitors of phosphoethanolamine Methyltransferases in Haemonchus contortus.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2016 Jan 18;6(1):44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2016.01.002. eCollection 2016 Apr. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2016. PMID: 27054063 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoethanolamine methyltransferases in phosphocholine biosynthesis: functions and potential for antiparasite therapy.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011 Jul;35(4):609-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00267.x. Epub 2011 Mar 10. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21303393 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of phosphoethanolamine methyltransferase from Plasmodium falciparum in complex with amodiaquine.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Aug 1;22(15):4990-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.06.032. Epub 2012 Jun 17. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22771008 Free PMC article.
-
Antimalarial agents against both sexual and asexual parasites stages: structure-activity relationships and biological studies of the Malaria Box compound 1-[5-(4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)furan-2-yl]-N-[(piperidin-4-yl)methyl]methanamine (MMV019918) and analogues.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Apr 25;150:698-718. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.03.024. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29571157 Free PMC article.
-
Nematode phospholipid metabolism: an example of closing the genome-structure-function circle.Trends Parasitol. 2014 May;30(5):241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Trends Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24685202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of structure and mechanistic divergence in di-domain methyltransferases from nematode phosphocholine biosynthesis.Structure. 2013 Oct 8;21(10):1778-87. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.07.023. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Structure. 2013. PMID: 24012478 Free PMC article.
-
An alternative mechanism for the methylation of phosphoethanolamine catalyzed by Plasmodium falciparum phosphoethanolamine methyltransferase.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 5;289(49):33815-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.611319. Epub 2014 Oct 6. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25288796 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

