microRNA-101 is a potent inhibitor of autophagy
- PMID: 21915098
- PMCID: PMC3243595
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.331
microRNA-101 is a potent inhibitor of autophagy
Abstract
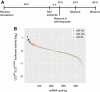
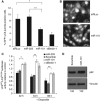
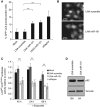
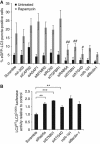
Autophagy is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism of cellular self-digestion in which proteins and organelles are degraded through delivery to lysosomes. Defects in this process are implicated in numerous human diseases including cancer. To further elucidate regulatory mechanisms of autophagy, we performed a functional screen in search of microRNAs (miRNAs), which regulate the autophagic flux in breast cancer cells. In this study, we identified the tumour suppressive miRNA, miR-101, as a potent inhibitor of basal, etoposide- and rapamycin-induced autophagy. Through transcriptome profiling, we identified three novel miR-101 targets, STMN1, RAB5A and ATG4D. siRNA-mediated depletion of these genes phenocopied the effect of miR-101 overexpression, demonstrating their importance in autophagy regulation. Importantly, overexpression of STMN1 could partially rescue cells from miR-101-mediated inhibition of autophagy, indicating a functional importance for this target. Finally, we show that miR-101-mediated inhibition of autophagy can sensitize breast cancer cells to 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT)-mediated cell death. Collectively, these data establish a novel link between two highly important and rapidly growing research fields and present a new role for miR-101 as a key regulator of autophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

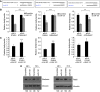
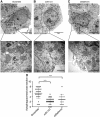
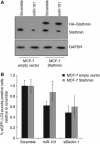
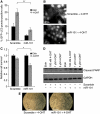
Comment in
-
Autophagy regulation by miRNAs: when cleaning goes out of service.EMBO J. 2011 Nov 16;30(22):4517-9. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.387. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 22085996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abedin MJ, Wang D, McDonnell MA, Lehmann U, Kelekar A (2007) Autophagy delays apoptotic death in breast cancer cells following DNA damage. Cell Death Differ 14: 500–510 - PubMed
-
- Alexa A, Rahnenfuhrer J, Lengauer T (2006) Improved scoring of functional groups from gene expression data by decorrelating GO graph structure. Bioinformatics 22: 1600–1607 - PubMed
-
- Alli E, Yang JM, Ford JM, Hait WN (2007a) Reversal of stathmin-mediated resistance to paclitaxel and vinblastine in human breast carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol 71: 1233–1240 - PubMed
-
- Alli E, Yang JM, Hait WN (2007b) Silencing of stathmin induces tumor-suppressor function in breast cancer cell lines harboring mutant p53. Oncogene 26: 1003–1012 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

