Splicing factor hnRNPH drives an oncogenic splicing switch in gliomas
- PMID: 21915099
- PMCID: PMC3209773
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.259
Splicing factor hnRNPH drives an oncogenic splicing switch in gliomas
Abstract
In tumours, aberrant splicing generates variants that contribute to multiple aspects of tumour establishment, progression and maintenance. We show that in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) specimens, death-domain adaptor protein Insuloma-Glucagonoma protein 20 (IG20) is consistently aberrantly spliced to generate an antagonist, anti-apoptotic isoform (MAP-kinase activating death domain protein, MADD), which effectively redirects TNF-α/TRAIL-induced death signalling to promote survival and proliferation instead of triggering apoptosis. Splicing factor hnRNPH, which is upregulated in gliomas, controls this splicing event and similarly mediates switching to a ligand-independent, constitutively active Recepteur d'Origine Nantais (RON) tyrosine kinase receptor variant that promotes migration and invasion. The increased cell death and the reduced invasiveness caused by hnRNPH ablation can be rescued by the targeted downregulation of IG20/MADD exon 16- or RON exon 11-containing variants, respectively, using isoform-specific knockdown or splicing redirection approaches. Thus, hnRNPH activity appears to be involved in the pathogenesis and progression of malignant gliomas as the centre of a splicing oncogenic switch, which might reflect reactivation of stem cell patterns and mediates multiple key aspects of aggressive tumour behaviour, including evasion from apoptosis and invasiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

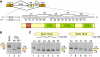
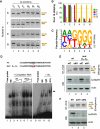




Comment in
-
Gene expression: Variety is the splice of strife.Nat Rev Cancer. 2011 Oct 7;11(11):759. doi: 10.1038/nrc3156. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21979305 No abstract available.
References
-
- Al-Zoubi AM, Efimova EV, Kaithamana S, Martinez O, El-Idrissi Mel A, Dogan RE, Prabhakar BS (2001) Contrasting effects of IG20 and its splice isoforms, MADD and DENN-SV, on tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis and activation of caspase-8 and -3. J Biol Chem 276: 47202–47211 - PubMed
-
- Bredel M, Bredel C, Juric D, Harsh GR, Vogel H, Recht LD, Sikic BI (2005) Functional network analysis reveals extended gliomagenesis pathway maps and three novel MYC-interacting genes in human gliomas. Cancer Res 65: 8679–8689 - PubMed
-
- Camacho-Vanegas O, Narla G, Teixeira MS, DiFeo A, Misra A, Singh G, Chan AM, Friedman SL, Feuerstein BG, Martignetti JA (2007) Functional inactivation of the KLF6 tumor suppressor gene by loss of heterozygosity and increased alternative splicing in glioblastoma. Int J Cancer 121: 1390–1395 - PubMed
-
- Caputi M, Zahler AM (2001) Determination of the RNA binding specificity of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) H/H′/F/2H9 family. J Biol Chem 276: 43850–43859 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

