Effects of thyroxine replacement on endothelial function and carotid artery intima-media thickness in female patients with mild subclinical hypothyroidism
- PMID: 21915478
- PMCID: PMC3161206
- DOI: 10.1590/s1807-59322011000800003
Effects of thyroxine replacement on endothelial function and carotid artery intima-media thickness in female patients with mild subclinical hypothyroidism
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have suggested an association between subclinical hypothyroidism and coronary artery disease that could be related to changes in serum lipids or endothelial dysfunction.
Methods: Thirty-two female subclinical hypothyroidism patients were randomly assigned to 12 months of L-thyroxine replacement or no treatment. Endothelial function was measured by the flow-mediated vasodilatation of the brachial artery, as well as mean carotid artery intima-media thickness, and lipid profiles were studied at baseline and after 12 months of follow-up.
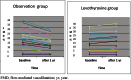
Results: The mean ( ± SD) serum thyroid-stimulating hormone levels in the L-thyroxine replacement and control groups were 6.09 ± 1.32 and 6.27 ± 1.39 μUI/ml, respectively. No relationship between carotid artery intima-media thickness or brachial flow-mediated vasodilatation and free T4 and serum thyroid-stimulating hormone was found. The median L-T4 dose was 44.23 ± 18.13 μg/day. After 12 months, there was a significant decrease in the flow-mediated vasodilatation in the subclinical hypothyroidism control group (before: 17.33 ± 7.88 to after: 13.1 ± 4.75%, p =0.03), but there were no significant differences in flow-mediated vasodilatation in the L-thyroxine treated group (before: 16.81 ± 7.0 to after: 18.52 ± 7.44%, p = 0.39). We did not find any significant change in mean carotid intimamedia thickness after 12 months of L-thyroxine treatment.
Conclusion: Replacement therapy prevents a decline in flow-mediated vasodilatation with continuation of the subclinical hypothyroidism state. Large prospective multicenter placebo-controlled trials are necessary to investigate endothelial physiology further in subclinical hypothyroidism patients and to define the role of L-thyroxine therapy in improving endothelial function in these patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of levothyroxine on the progression of carotid intima-media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism patients: a meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2017 Oct 22;7(10):e016053. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016053. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 29061604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in arterial stiffness, carotid intima-media thickness, and epicardial fat after L-thyroxine replacement therapy in hypothyroidism.Endocrinol Nutr. 2015 Jun-Jul;62(6):270-6. doi: 10.1016/j.endonu.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Endocrinol Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25882083 English, Spanish.
-
Effects of 18 months of L-T4 replacement in women with subclinical hypothyroidism.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009 Aug;71(2):298-303. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2008.03509.x. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009. PMID: 19094068 Clinical Trial.
-
Normal flow-mediated vasodilatation of the brachial artery and carotid artery intima-media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2009 May;42(5):426-32. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2009000500005. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2009. PMID: 19377791
-
Subclinical hypothyroidism, lipid metabolism and cardiovascular disease.Eur J Intern Med. 2017 Mar;38:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2016.12.015. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Eur J Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28040402 Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelial dysfunction and the risk of atherosclerosis in overt and subclinical hypothyroidism.Endocr Connect. 2018 Oct 1;7(10):1075-1080. doi: 10.1530/EC-18-0194. Endocr Connect. 2018. PMID: 30352390 Free PMC article.
-
Study protocol; Thyroid hormone Replacement for Untreated older adults with Subclinical hypothyroidism - a randomised placebo controlled Trial (TRUST).BMC Endocr Disord. 2017 Feb 3;17(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12902-017-0156-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2017. PMID: 28158982 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of levothyroxine on the progression of carotid intima-media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism patients: a meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2017 Oct 22;7(10):e016053. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016053. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 29061604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Pattern of Dyslipidemia Associated with Iodine Deficiency and Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Pregnant Normotensive and Preeclamptic Central African Women.Pathophysiology. 2025 Apr 18;32(2):18. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology32020018. Pathophysiology. 2025. PMID: 40265443 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering thyroid function and CIMT: a Mendelian randomization study of the U-shaped influence mediated by apolipoproteins.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Mar 22;15:1345267. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1345267. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38586463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayala A, Wartofsky L. Minimally symptomatic (subclinical) hypothyroidism. The Endocrinologist. 1997;7:44–50.
-
- Canaris GJ, Manowitz NR, Mayor G, Ridgway EC. The Colorado thyroid disease prevalence study. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:526–34. - PubMed
-
- Cooper DS. Clinical practice. Subclinical hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:260–5. - PubMed
-
- Rodondi NR, Aujesky D, Vittinghoff A, Cornus J, Bauer D. Subclinical hypothyroidism and the risk of coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2006;119:541–51. - PubMed
-
- Ochs N, Auer R, Bauer D, Nanchen D, Gussekloo J, Cornuz J, et al. Meta-analysis: subclinical thyroid dysfunction and the risk for coronary heart disease and mortality. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:832–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical