The Xanthomonas type III effector XopD targets the Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB30 to suppress plant defense
- PMID: 21917550
- PMCID: PMC3203416
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.111.088815
The Xanthomonas type III effector XopD targets the Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB30 to suppress plant defense
Erratum in
- Plant Cell. 2011 Oct;23(10):3866
-
Correction.Plant Cell. 2011 Nov 15;23(10):3866. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.231060. Online ahead of print. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 22086089 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Retraction in
-
RETRACTION.Plant Cell. 2018 Jan;30(1):253. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00567. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Plant Cell. 2018. PMID: 29255113 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Plant and animal pathogens inject type III effectors (T3Es) into host cells to suppress host immunity and promote successful infection. XopD, a T3E from Xanthomonas campestris pv vesicatoria, has been proposed to promote bacterial growth by targeting plant transcription factors and/or regulators. Here, we show that XopD from the B100 strain of X. campestris pv campestris is able to target MYB30, a transcription factor that positively regulates Arabidopsis thaliana defense and associated cell death responses to bacteria through transcriptional activation of genes related to very-long-chain fatty acid (VLCFA) metabolism. XopD specifically interacts with MYB30, resulting in inhibition of the transcriptional activation of MYB30 VLCFA-related target genes and suppression of Arabidopsis defense. The helix-loop-helix domain of XopD is necessary and sufficient to mediate these effects. These results illustrate an original strategy developed by Xanthomonas to subvert plant defense and promote development of disease.
Figures
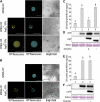
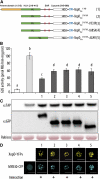
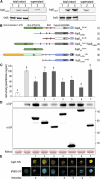

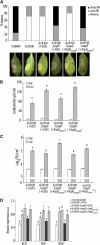
References
-
- Alfano J.R., Collmer A. (2004). Type III secretion system effector proteins: Double agents in bacterial disease and plant defense. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 42: 385–414 - PubMed
-
- Buell C.R., Somerville S.C. (1997). Use of Arabidopsis recombinant inbred lines reveals a monogenic and a novel digenic resistance mechanism to Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris. Plant J. 12: 21–29 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

