Direct structural analysis of modified RNA by fluorescent in-line probing
- PMID: 21917852
- PMCID: PMC3258135
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr733
Direct structural analysis of modified RNA by fluorescent in-line probing
Abstract
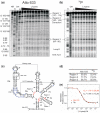
Chemical probing is a common method for the structural characterization of RNA. Typically, RNA is radioactively end-labelled, subjected to probing conditions, and the cleavage fragment pattern is analysed by gel electrophoresis. In recent years, many chemical modifications, like fluorophores, were introduced into RNA, but methods are lacking that detect the influence of the modification on the RNA structure with single-nucleotide resolution. Here, we first demonstrate that a 5'-terminal (32)P label can be replaced by a dye label for in-line probing of riboswitch RNAs. Next, we show that small, highly structured FRET-labelled Diels-Alderase ribozymes can be directly probed, using the internal or terminal FRET dyes as reporters. The probing patterns indeed reveal whether or not the attachment of the dyes influences the structure. The existence of two dye labels in typical FRET constructs is found to be beneficial, as 'duplexing' allows observation of the complete RNA on a single gel. Structural information can be derived from the probing gels by deconvolution of the superimposed band patterns. Finally, we use fluorescent in-line probing to experimentally validate the structural consequences of photocaging, unambiguously demonstrating the intentional destruction of selected elements of secondary or tertiary structure.
Figures



References
-
- Stern S, Moazed D, Noller HF. Structural analysis of RNA using chemical and enzymatic probing monitored by primer extension. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:481–489. - PubMed
-
- Forconi M, Herschlag D. Metal ion-based RNA cleavage as a structural probe. Methods Enzymol. 2009;468:91–106. - PubMed
-
- Sigel RK, Vaidya A, Pyle AM. Metal ion binding sites in a group II intron core. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000;7:1111–1116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

