Vaccine-induced cross-genotype reactive neutralizing antibodies against hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 21917891
- PMCID: PMC3203383
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jir511
Vaccine-induced cross-genotype reactive neutralizing antibodies against hepatitis C virus
Abstract
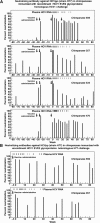
We detected cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies (NtAb) against hepatitis C virus (HCV) in chimpanzees vaccinated with HCV-1 (genotype 1a) recombinant E1/E2 envelope glycoproteins. Five vaccinated chimpanzees, protected following HCV-1 challenge, were initially studied using the heterologous H77 (genotype 1a) HCVpp assay. All animals had developed NtAb after the second vaccination; 4 animals had reciprocal titers of ≥200 at the time of challenge. Using genotypes 1a-6a HCV pseudoparticles (HCVpp) and cell culture-derived HCV (HCVcc) assays, cross-reactive NtAb were detected against 1a, 4a, 5a, and 6a, with limited reactivity against 2a and 3a. Our study provides encouragement for the development of a recombinant envelope-based vaccine against hepatitis C.
Figures
References
-
- Feray C, Gigou M, Samuel D, et al. Incidence of hepatitis C in patients receiving different preparations of hepatitis B immunoglobulins after liver transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128:810–6. - PubMed
-
- Knodell RG, Conrad ME, Ginsberg AL, Bell CJ. Efficacy of prophylactic gamma-globulin in preventing non-A, non-B post-transfusion hepatitis. Lancet. 1976;1:557–61. - PubMed
-
- Houghton M. Prospects for prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines against the hepatitis C viruses. Immunol Rev. 2011;239:99–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

