Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease
- PMID: 21917992
- PMCID: PMC3225943
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005058
Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease
Abstract
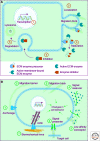
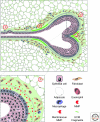
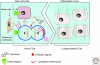
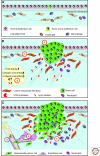
The extracellular matrix (ECM) serves diverse functions and is a major component of the cellular microenvironment. The ECM is a highly dynamic structure, constantly undergoing a remodeling process where ECM components are deposited, degraded, or otherwise modified. ECM dynamics are indispensible during restructuring of tissue architecture. ECM remodeling is an important mechanism whereby cell differentiation can be regulated, including processes such as the establishment and maintenance of stem cell niches, branching morphogenesis, angiogenesis, bone remodeling, and wound repair. In contrast, abnormal ECM dynamics lead to deregulated cell proliferation and invasion, failure of cell death, and loss of cell differentiation, resulting in congenital defects and pathological processes including tissue fibrosis and cancer. Understanding the mechanisms of ECM remodeling and its regulation, therefore, is essential for developing new therapeutic interventions for diseases and novel strategies for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Affolter M, Caussinus E 2008. Tracheal branching morphogenesis in Drosophila: New insights into cell behaviour and organ architecture. Development 135: 2055–2064 - PubMed
-
- Aiken A, Khokha R 2009. Unraveling metalloproteinase function in skeletal biology and disease using genetically altered mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803: 121–132 - PubMed
-
- Aitken KJ, Bagli DJ 2009. The bladder extracellular matrix. Part I: Architecture, development and disease. Nat Rev Urol 6: 596–611 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
