Characteristics of sodium currents in rat geniculate ganglion neurons
- PMID: 21917997
- PMCID: PMC3234091
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00369.2011
Characteristics of sodium currents in rat geniculate ganglion neurons
Abstract
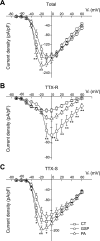
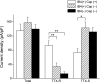
Geniculate ganglion (GG) cell bodies of chorda tympani (CT), greater superficial petrosal (GSP), and posterior auricular (PA) nerves transmit orofacial sensory information to the rostral nucleus of the solitary tract. We have used whole cell recording to investigate the characteristics of the Na(+) channels in isolated Fluorogold-labeled GG neurons that innervate different peripheral receptive fields. GG neurons expressed two classes of Na(+) channels, TTX sensitive (TTX-S) and TTX resistant (TTX-R). The majority of GG neurons expressed TTX-R currents of different amplitudes. TTX-R currents were relatively small in 60% of the neurons but were large in 12% of the sampled population. In a further 28% of the neurons, TTX completely abolished all Na(+) currents. Application of TTX completely inhibited action potential generation in all CT and PA neurons but had little effect on the generation of action potentials in 40% of GSP neurons. Most CT, GSP, and PA neurons stained positively with IB(4), and 27% of the GSP neurons were capsaicin sensitive. The majority of IB(4)-positive GSP neurons with large TTX-R Na(+) currents responded to capsaicin, whereas IB(4)-positive GSP neurons with small TTX-R Na(+) currents were capsaicin insensitive. These data demonstrate the heterogeneity of GG neurons and indicate the existence of a subset of GSP neurons sensitive to capsaicin, usually associated with nociceptors. Since there are no reports of nociceptors in the GSP receptive field, the role of these capsaicin-sensitive neurons is not clear.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Characteristics of calcium currents in rat geniculate ganglion neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2011 Jan;105(1):224-34. doi: 10.1152/jn.00636.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Neurophysiol. 2011. PMID: 21068265 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive Na+ current, TTX-resistant Na+ current, and Ca2+ current in the action potentials of nociceptive sensory neurons.J Neurosci. 2002 Dec 1;22(23):10277-90. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-23-10277.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12451128 Free PMC article.
-
Functional tetrodotoxin-resistant Na(+) channels are expressed presynaptically in rat dorsal root ganglia neurons.Neuroscience. 2009 Mar 17;159(2):559-69. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.12.029. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19162133
-
Analysis of the variation in use-dependent inactivation of high-threshold tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium currents recorded from rat sensory neurons.Neuroscience. 2006 Dec 28;143(4):923-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.08.052. Epub 2006 Oct 4. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 17027172
-
Ketamine blockage of both tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive and TTX-resistant sodium channels of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons.Brain Res Bull. 2000 Jul 15;52(5):427-33. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(00)00283-5. Brain Res Bull. 2000. PMID: 10922523
Cited by
-
Taste buds: cells, signals and synapses.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017 Aug;18(8):485-497. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.68. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28655883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRPs in taste and chemesthesis.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;223:827-71. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-05161-1_5. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24961971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptive field size, chemical and thermal responses, and fiber conduction velocity of rat chorda tympani geniculate ganglion neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Jun 1;115(6):3062-72. doi: 10.1152/jn.00045.2016. Epub 2016 Mar 30. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27030734 Free PMC article.
-
A 3.7 kb fragment of the mouse Scn10a gene promoter directs neural crest but not placodal lineage EGFP expression in a transgenic animal.J Neurosci. 2015 May 20;35(20):8021-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0214-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25995484 Free PMC article.
-
Oral thermosensing by murine trigeminal neurons: modulation by capsaicin, menthol and mustard oil.J Physiol. 2019 Apr;597(7):2045-2061. doi: 10.1113/JP277385. Epub 2019 Feb 10. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30656684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arai T, Ohkuri T, Yasumatsu K, Kaga T, Ninomiya Y. The role of transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 on neural responses to acids by the chorda tympani, glossopharyngeal and superior laryngeal nerves in mice. Neuroscience 165: 1476–1489, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Bossu JL, Feltz A. Patch-clamp study of the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium current in group C sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett 51: 241–246, 1984 - PubMed
-
- Boudreau JC, Bradley BE, Bierer PR, Kruger S, Tsuchitani C. Single unit recordings from the geniculate ganglion of the facial nerve of the cat. Exp Brain Res 13: 461–488, 1971 - PubMed
-
- Breza JM, Curtis KS, Contreras RJ. Temperature modulates taste responsiveness and stimulates gustatory neurons in the rat geniculate ganglion. J Neurophysiol 95: 674–685, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Carlton SM, Hargett GL. Stereological analysis of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIα-containing dorsal root ganglion neurons in the rat: colocalization with isolectin Griffonia simplicifolia, calcitonin gene-related peptide, or vanilloid receptor 1. J Comp Neurol 448: 102–110, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

